49 5.9 Regulation of Gene Expression
Created by: CK-12/Adapted by Christine Miller
Express Yourself
This sketch illustrates some of the variability in human cells. The shape and other characteristics that make each type of cell unique depend mainly on the specific proteins that particular cell type makes. Proteins are encoded in genes. All the cells in an organism have the same genes, so they all have genetic instructions for the same proteins. Obviously, different types of cells must use (or express) different genes to make different proteins.
What Is Gene Expression?
Using a gene to make a protein is called gene expression. It includes the synthesis of the protein by the processes of transcription of DNA into mRNA, and translation of mRNA into a protein. It may also include further processing of the protein after synthesis.
Gene expression is regulated to ensure that the correct proteins are made when and where they are needed. Regulation may occur at any point in the expression of a gene, from the start of the transcription phase of protein synthesis to the processing of a protein after synthesis occurs. The regulation of transcription is one of the most complicated parts of gene regulation in eukaryotic cells, and it is the focus of this concept.
Regulation of Transcription
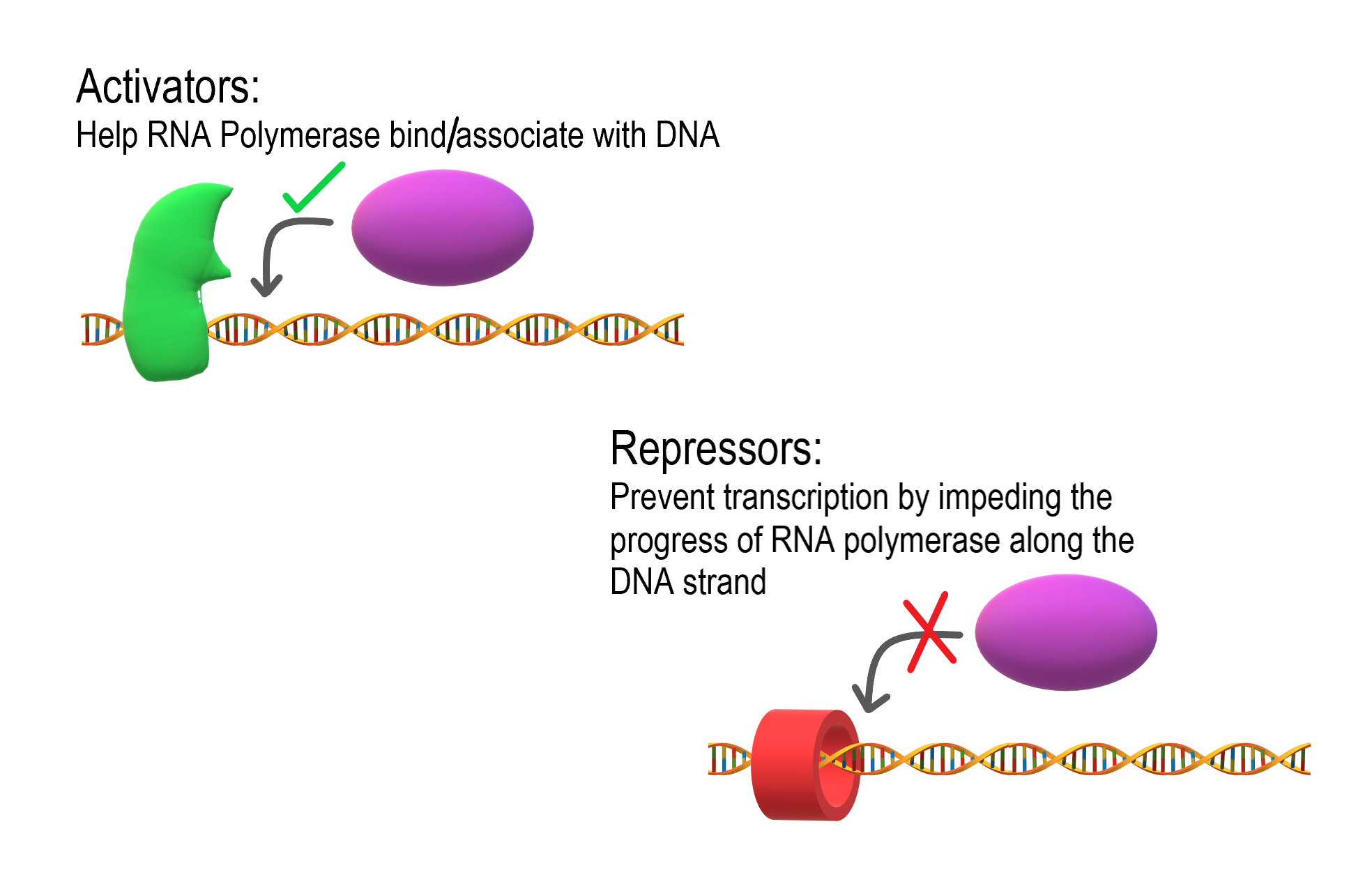
As shown in Figure 5.9.2, transcription is controlled by regulatory proteins. These proteins bind to regions of DNA, called regulatory elements, which are located near promoters. The promoter is the region of a gene where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription of the DNA to mRNA. After regulatory proteins bind to regulatory elements, the proteins can interact with RNA polymerase. Regulatory proteins are typically either activators or repressors. Activators are regulatory proteins that promote transcription by enhancing the interaction of RNA polymerase with the promoter. Repressors are regulatory proteins that prevent transcription by impeding the progress of RNA polymerase along the DNA strand, so the DNA cannot be transcribed to mRNA.
Enhancers
Although regulatory proteins and elements are typically the key players in the regulation of transcription, other factors may also be involved. Regulation of transcription may also involve enhancers. Enhancers are distant regions of DNA that can loop back to interact with a gene’s promoter. They can also increase the likelihood that transcription of the gene will occur.Enhancers
The TATA Box
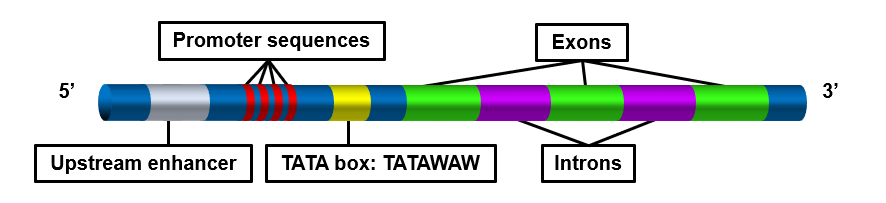
Different types of cells have unique patterns of regulatory elements that result in only the necessary genes being transcribed. That’s why a blood cell and nerve cell, for example, are so different from each other. Some regulatory elements, however, are common to virtually all genes, regardless of the cells in which they occur. An example is the TATA box, which is a regulatory element that is part of the promoter of almost every eukaryotic gene. A number of regulatory proteins bind to the TATA box, forming a multi-protein complex. It is only when all of the appropriate proteins are bound to the TATA box that RNA polymerase recognizes the complex and binds to the promoter so transcription can begin.
Regulation During Development
The regulation of gene expression is extremely important in an organism’s early development. Regulatory proteins must “turn on” certain genes in particular cells at just the right time, so the individual develops normal organs and organ systems. Homeobox genes are important genes that regulate development.
Homeobox genes are a large group of similar genes that direct the formation of many body structures during the embryonic stage. In humans, there are an estimated 235 functional homeobox genes. They are present on every chromosome and generally grouped in clusters. Homeobox genes contain instructions for making chains of 60 amino acids, called homeodomains. Proteins containing homeodomains are transcription factors that bind to and control the activities of other genes. The homeodomain is the part of the protein that binds to the target gene and controls its expression.
Gene Expression and Cancer
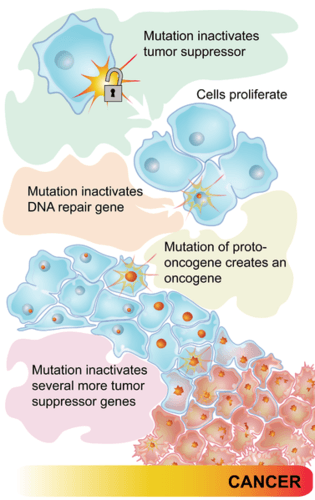
Some types of cancer occur because of mutations in the genes that control the cell cycle. Cancer-causing mutations most often occur in two types of regulatory genes: proto-oncogenes and tumor-suppressor genes. Both are shown in Figure 5.9.4.
- Proto-oncogenes are genes that normally help cells divide. When a proto-oncogene mutates to become an oncogene, it is continuously expressed, even when it is not supposed to be. This is like a car’s accelerator pedal being stuck at full throttle. The car keeps racing at top speed. A cell, in this case, keeps dividing out of control, which can lead to cancer.
- Tumor suppressor genes are genes that normally slow down or stop cell division. When a mutation occurs in a tumor suppressor gene, it can no longer control cell division. This is like a car without brakes. The car can’t be slowed or stopped. A cell, in this case, keeps dividing out of control, which can lead to cancer.
5.9 Summary
- Using a gene to make a protein is called gene expression. Gene expression is regulated to ensure that the correct proteins are made when and where they are needed. Regulation may occur at any stage of protein synthesis or processing.
- The regulation of transcription is controlled by regulatory proteins that bind to regions of DNA called regulatory elements, which are usually located near promoters. Most regulatory proteins are either activators that promote transcription, or repressors that impede transcription.
- A regulatory element common to almost all eukaryotic genes is the TATA box. A number of regulatory proteins must bind to the TATA box in the promoter before transcription can proceed.
- Regulation of gene expression is extremely important during an organism’s early development. Homeobox genes — which encode for chains of amino acids called homeodomains — are important genes that regulate development.
- Some types of cancer occur because of mutations in the genes that control the cell cycle. Cancer-causing mutations most often occur in two types of regulatory genes: tumor-suppressor genes and proto-oncogenes.
5.9 Review Questions
- Define gene expression.
- Why must gene expression be regulated?
- Explain how regulatory proteins may activate or repress transcription.
-
- What is the TATA box, and how does it work?
- Describe homeobox genes and their role in an organism’s development.
- Discuss the role of regulatory gene mutations in cancer.
- Explain the relationship between proto-oncogenes and oncogenes.
- If a newly fertilized egg contained a mutation in a homeobox gene, how do you think this would affect the developing embryo? Explain your answer.
- Compare and contrast enhancers and activators.
5.9 Explore More
Regulated Transcription, ndsuvirtualcell, 2008.
How do cancer cells behave differently from healthy ones? – George Zaidan,
TED-Ed, 2012.
What is leukemia? – Danilo Allegra and Dania Puggioni, 2015.
Attributions
Figure 5.9.1
Stem_cell_differentiation.svg by Haileyfournier on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 5.9.2
Activators and Repressors by Christine Miller is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 5.9.3
TATA_box_description by Luttysar on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 5.9.4
Pathways to cancer by CK-12 Foundation is used under a CC BY-NC 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) license.
 ©CK-12 Foundation Licensed under
©CK-12 Foundation Licensed under ![]() • Terms of Use • Attribution
• Terms of Use • Attribution
References
Brainard, J/ CK-12 Foundation. (2012). Figure 3 Flow chart (series of mutations leading to cancer) [digital image]. In CK-12 College Human Biology (Section 5.8) [online Flexbook]. CK12.org. https://www.ck12.org/c/physical-science/concentration/?referrer=crossref
ndsuvirtualcell.(2008). Regulated transcription. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vi-zWoobt_Q&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2012, December 5). How do cancer cells behave differently from healthy ones? – George Zaidan. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BmFEoCFDi-w&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2015, April 15). What is leukemia? – Danilo Allegra and Dania Puggioni. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z3B-AaqjyjE&feature=youtu.be
The smallest unit of life, consisting of at least a membrane, cytoplasm, and genetic material.
A sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA that codes for a molecule that has a function.
A class of biological molecule consisting of linked monomers of amino acids and which are the most versatile macromolecules in living systems and serve crucial functions in essentially all biological processes.
The process by which DNA is copied (transcribed) to mRNA in order transfer the information needed for protein synthesis.
Deoxyribonucleic acid - the molecule carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.
A large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression.
The process in which mRNA along with transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomes work together to produce polypeptides.
Cells which have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, unlike prokaryotes, which have no membrane-bound organelles.
Any protein that influences the regions of a DNA molecule that are transcribed by RNA polymerase during the process of transcription.
Regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes.
A sequence of DNA to which proteins bind that initiate transcription of a single mRNA from the DNA downstream of it.
Regulatory proteins that promote transcription by enhancing the interaction of RNA polymerase with the promoter.
Regulatory proteins that prevent transcription by impeding the progress of RNA polymerase along the DNA strand, so the DNA cannot be transcribed to mRNA.
Regulatory DNA sequences that, when bound by specific proteins called transcription factors, enhance the transcription of an associated gene.
A DNA sequence that indicates where a genetic sequence can be read and decoded. It is a type of promoter sequence, which specifies to other molecules where transcription begins.
A large group of similar genes that direct the formation of many body structures during early embryonic development.
An early stage of development of a multicellular organism. In general, in organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development refers to the portion of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization and continues through the formation of body structures, such as tissues and organs.
Amino acids are organic compounds that combine to form proteins.
The part of a protein that attaches (binds) to specific regulatory regions of the target genes.
A group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body.
The process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional protein.
The process of creating protein molecules.
An alteration in the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism.
A cycle of growth and division that cells go through. It includes interphase (G1, S, and G2) and the mitotic phase.

