55 5.15 Genetic Disorders
Created by: CK-12/Adapted by Christine Miller
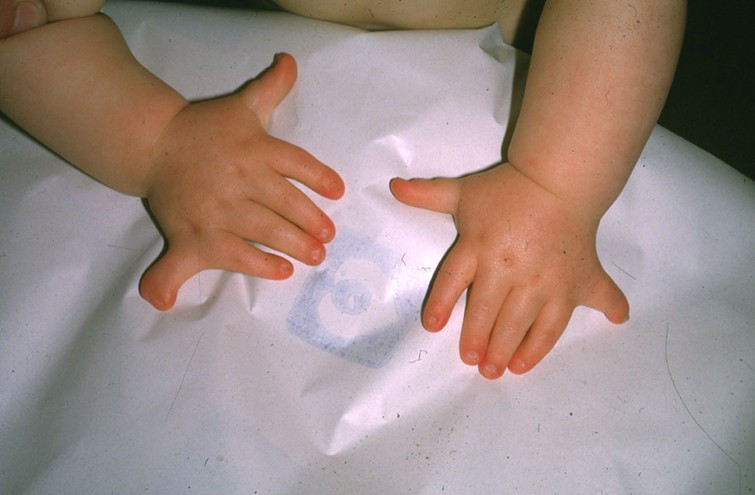
Polly Who?
Each hand in the Figure 5.15.1 photo has an extra pinky finger. This is a condition called polydactyly, which literally means “many digits.” People with polydactyly may have extra fingers and/or toes, and the condition may affect just one hand or foot, or both hands and feet. Polydactyly is often genetic in origin and may be part of a genetic disorder associated with other abnormalities.
What Are Genetic Disorders?
Genetic disorders are diseases, syndromes, or other abnormal conditions caused by mutations in one or more genes, or by chromosomal alterations. Genetic disorders are typically present at birth, but they should not be confused with congenital disorders, a category that includes any disorder present at birth, regardless of cause. Some congenital disorders are not caused by genetic mutations or chromosomal alterations. Instead, they are caused by problems that arise during embryonic or fetal development, or during the process of birth. An example of a nongenetic congenital disorder is fetal alcohol syndrome. This is a collection of birth defects, including facial anomalies and intellectual disability, caused by maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
Genetic Disorders Caused by Mutations
Table 5.15.1 lists several genetic disorders caused by mutations in just one gene. Some of the disorders are caused by mutations in autosomal genes, others by mutations in X-linked genes. Which disorders would you expect to be more common in males than females?
| Genetic Disorder | Direct Effect of Mutation | Signs and Symptoms of the Disorder | Mode of Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marfan syndrome | Defective protein in connective tissue | Heart and bone defects and unusually long, slender limbs and fingers | Autosomal dominant |
| Sickle cell anemia | Abnormal hemoglobin protein in red blood cells | Sickle-shaped red blood cells that clog tiny blood vessels, causing pain and damaging organs and joints | Autosomal recessive |
| Hypophosphatemic (Vitamin D-resistant) rickets | Lack of a substance needed for bones to absorb minerals | Soft bones that easily become deformed, leading to bowed legs and other skeletal deformities | X-linked dominant |
| Hemophilia A | Reduced activity of a protein needed for blood clotting | Internal and external bleeding that occurs easily and is difficult to control | X-linked recessive |
Very few genetic disorders are controlled by dominant mutant [pHypophosphatemicb_glossary id=”2119″]alleles[/pb_glossary]. A dominant allele is expressed in every individual who inherits even one copy of it. If it causes a serious disorder, affected people may die young and fail to reproduce. Therefore, the mutant dominant allele is likely to die out of a population.
A recessive mutant allele — such as the allele that causes sickle cell anemia or cystic fibrosis — is not expressed in people who inherit just one copy of it. These people are called carriers. They do not have the disorder themselves, but they carry the mutant allele and their offspring can inherit it. Thus, the allele is likely to pass on to the next generation, rather than die out.
Genetic Disorders Caused by Chromosomal Alterations
Mistakes may occur during meiosis that result in nondisjunction. This is the failure of replicated chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis. Some of the resulting gametes will be missing all or part of a chromosome, while others will have an extra copy of all or part of the chromosome. If such gametes are fertilized and form zygotes, they usually do not survive. If they do survive, the individuals are likely to have serious genetic disorders.
Table 5.15.2 lists several genetic disorders that are caused by abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Most chromosomal disorders involve the X chromosome. The X and Y chromosomes are the only chromosome pair in which the two chromosomes are very different in size. This explains why nondisjunction tends to occur more frequently in sex chromosomes than in autosomes.
| Genetic Disorder | Genotype | Phenotypic Effects |
|---|---|---|
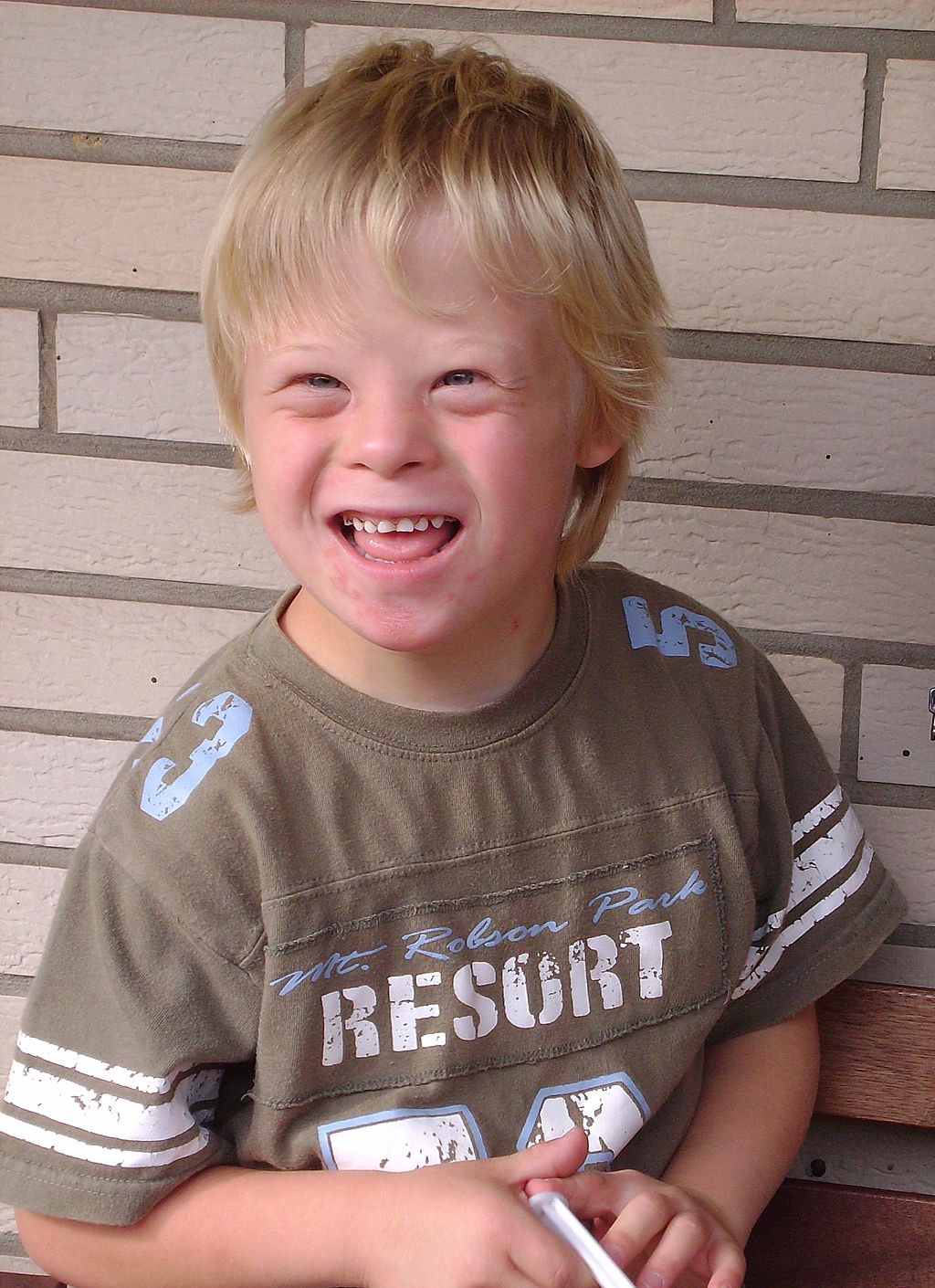
| Down syndrome | Extra copy (complete or partial) of chromosome 21 (see Figure 5.15.3) | Developmental delays, distinctive facial appearance, and other abnormalities (see Figure 5.15.2) |
| Turner syndrome | One X chromosome but no other sex chromosome (XO) | Female with short height and infertility(inability to reproduce) |
| Triple X syndrome | Three X chromosomes (XXX) | Female with mild developmental delays and menstrual irregularities |
| Klinefelter syndrome | One Y chromosome and two or more X chromosomes (XXY, XXXY) | Male with problems in sexual development and reduced levels of the male hormone testosterone |
 |
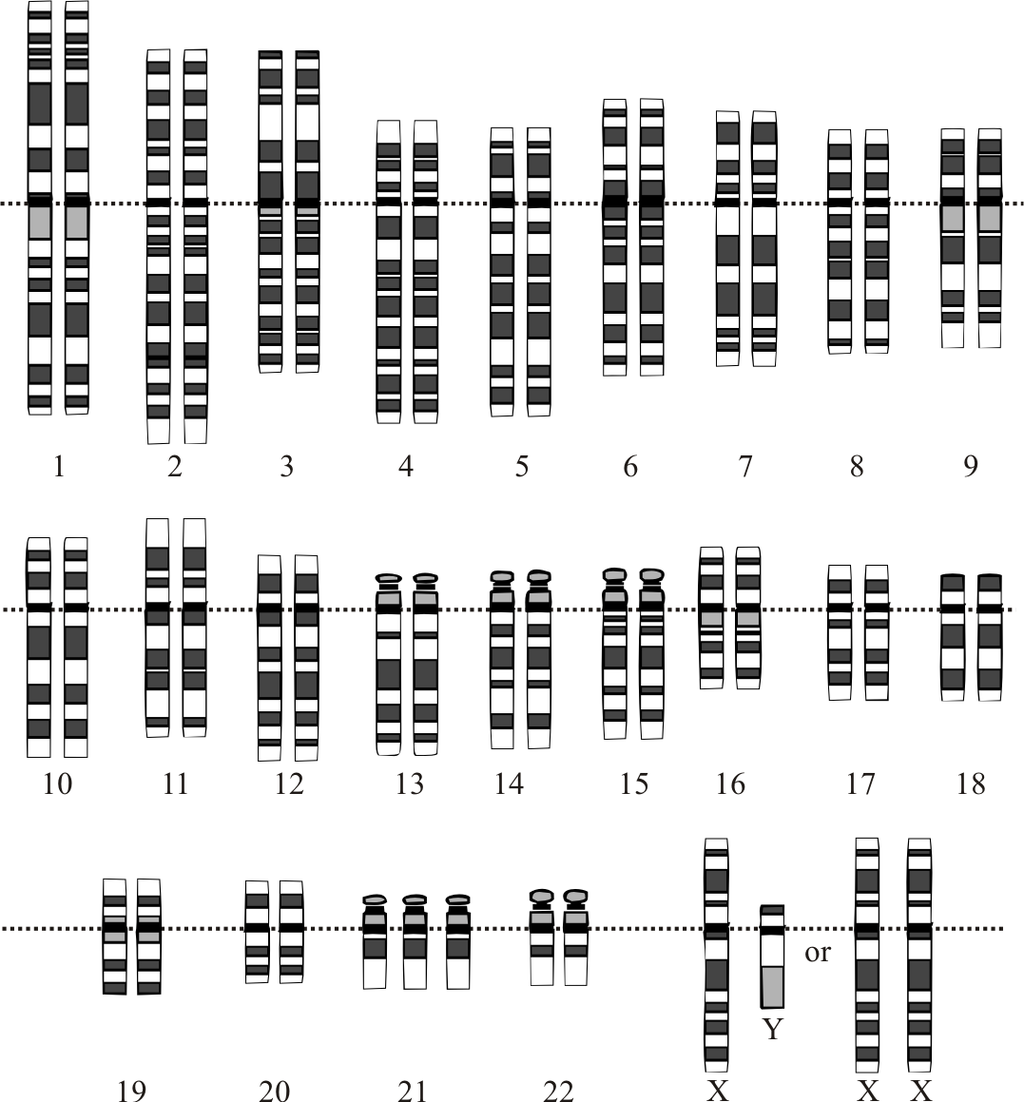 |
A karyotype is a picture of a cell’s chromosomes. In Figure 5.15.3, note the extra chromosome 21. In Figure 5.15.2, a young man with Down syndrome exhibits the characteristic facial appearance.
Diagnosing and Treating Genetic Disorders
A genetic disorder that is caused by a mutation can be inherited. Therefore, people with a genetic disorder in their family may be concerned about having children with the disorder. A genetic counselor can help them understand the risks of their children being affected. If they decide to have children, they may be advised to have prenatal (“before birth”) testing to see if the fetus has any genetic abnormalities. One method of prenatal testing is amniocentesis. In this procedure, a few fetal cells are extracted from the fluid surrounding the fetus in utero, and the fetal chromosomes are examined. Down syndrome and other chromosomal alterations can be detected in this way.
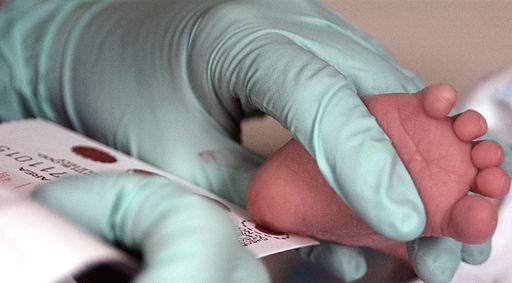
The symptoms of genetic disorders can sometimes be treated or prevented. In the genetic disorder called phenylketonuria (PKU), for example, the amino acid phenylalanine builds up in the body to harmful levels. PKU is caused by a mutation in a gene that normally codes for an enzyme needed to break down phenylalanine. When a person with PKU consumes foods high in phenylalanine (including many high-protein foods), the buildup of PKU can lead to serious health problems. In infants and young children, the build-up of phenylalanine can cause intellectual disability and delayed development, along with other serious problems. All babies in Canada and the United States and many other countries are screened for PKU soon after birth. As shown in Figure 5.15.3, the PKU test involves collecting a small amount of blood from the infant, typically from the heel using a small lancet. The blood is collected on a special type of filter paper and then brought to a laboratory for analysis. If PKU is diagnosed, the infant can be fed a low-phenylalanine diet, which prevents the buildup of phenylalanine and the health problems associated with it, including intellectual disability. As long as a low-phenylalanine diet is followed throughout life, most symptoms of the disorder can be prevented.
Curing Genetic Disorders
Cures for genetic disorders are still in the early stages of development. One potential cure is gene therapy. Gene therapy is an experimental technique that uses genes to treat or prevent disease. In gene therapy, normal genes are introduced into cells to compensate for abnormal genes. If a mutated gene causes a necessary protein to be nonfunctional or missing, gene therapy may be able to introduce a normal copy of the gene to produce the needed functional protein.
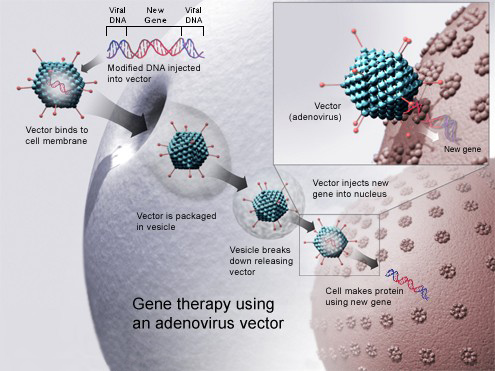
A gene inserted directly into a cell usually does not function, so a carrier called a vector is genetically engineered to deliver the gene (see Figure 5.15.4 illustration). Certain viruses, such as adenoviruses, are often used as vectors. They can deliver the new gene by infecting cells. The viruses are modified so they do not cause disease when used in people. If the treatment is successful, the new gene delivered by the vector will allow the synthesis of a functioning protein. Researchers still must overcome many technical challenges before gene therapy will be a practical approach to curing genetic disorders.
Feature: Human Biology in the News

Down syndrome is the most common genetic cause of intellectual disability. It occurs in about one in every 700 live births, and it currently affects nearly half a million Americans. Until recently, scientists thought that the changes leading to intellectual disability in people with Down syndrome all happen before birth.
Even more recently, researchers discovered a genetic abnormality that affects brain development in people with Down syndrome throughout childhood and into adulthood. The newly discovered genetic abnormality changes communication between nerve cells in the brain, resulting in slower transmission of nerve impulses. This finding may eventually allow the development of strategies to promote brain functioning in Down syndrome patients, and it may also be applicable to other development disabilities, such as autism. The results of this promising study were published in the March 16, 2016 issue of the scientific journal Neuron.
5.15 Summary
- Genetic disorders are diseases, syndromes, or other abnormal conditions that are caused by mutations in one or more genes, or by chromosomal alterations.
- Examples of genetic disorders caused by single-gene mutations include Marfan syndrome (autosomal dominant), sickle cell anemia (autosomal recessive), vitamin D-resistant rickets (X-linked dominant), and hemophilia A (X-linked recessive). Very few genetic disorders are caused by dominant mutations because these alleles are less likely to be passed on to successive generations.
- Nondisjunction is the failure of replicated chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis. This may result in genetic disorders caused by abnormal numbers of chromosomes. An example is Down syndrome, in which the individual inherits an extra copy of chromosome 21. Most chromosomal disorders involve the X chromosome. An example is Klinefelter’s syndrome (XXY, XXXY).
- Prenatal genetic testing (by amniocentesis, for example) can detect chromosomal alterations in utero. The symptoms of some genetic disorders can be treated or prevented. For example, symptoms of phenylketonuria (PKU) can be prevented by following a low-phenylalanine diet throughout life.
- Cures for genetic disorders are still in the early stages of development. One potential cure is gene therapy, in which normal genes are introduced into cells by a vector such as a virus to compensate for mutated genes.
5.15 Review Questions
- Define genetic disorder.
- Identify three genetic disorders caused by mutations in a single gene.
- Why are single-gene genetic disorders more commonly controlled by recessive than dominant mutant alleles?
- What is nondisjunction? Why can it cause genetic disorders?
- Explain why genetic disorders caused by abnormal numbers of chromosomes most often involve the X chromosome.
- How is Down syndrome detected in utero?
- Use the example of PKU to illustrate how the symptoms of a genetic disorder can sometimes be prevented.
- Explain how gene therapy works.
- Compare and contrast genetic disorders and congenital disorders.
- Explain why parents that do not have Down syndrome can have a child with Down syndrome.
- Hemophilia A and Turner’s syndrome both involve problems with the X chromosome. In terms of how the X chromosome is affected, what is the major difference between these two types of disorders?
- Can you be a carrier of Marfan syndrome and not have the disorder? Explain your answer.
5.15 Explore More
How CRISPR lets you edit DNA – Andrea M. Henle, TED-Ed, 2019.
What you need to know about CRISPR | Ellen Jorgensen, TED, 2016.
The ethical dilemma of designer babies | Paul Knoepfler, TED, 2017.
Attributions
Figure 5.15.1
Polydactyly_ECS by Baujat G, Le Merrer M. on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0) license.
Figure 5.15.2
Downs/ All the Family [photo] by Nathan Anderson on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 5.15.3
Phenylketonuria_testing by U.S. Air Force photo/Staff Sgt Eric T. Sheler in the US Air Force National Archives on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 5.15.4
Gene_therapy by National Institutes of Health (NIH) on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 5.15.5
Boy_with_Down_Syndrome by Vanellus Foto on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en) license.
References
Baujat, G., Le Merrer, M. (2007, January 23). Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 2, 27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-2-27
Hecht, M. (2019, June 26). What is polydactyly? [online article]. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/polydactyly
Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD). (2016). Hypophosphatemic rickets (previously called vitamin D-resistant rickets) [online article]. NIH. https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/6735/hypophosphatemic-rickets [last updated 7/1/2020]
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Cystic fibrosis [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cystic-fibrosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20353700
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Down syndrome [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/down-syndrome/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20355983
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Hemophilia [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hemophilia/symptoms-causes/syc-20373327
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Klinefelter syndrome [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/klinefelter-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20353949
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Marfan syndrome [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/marfan-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20350782
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Phenylketonuria (PKU) [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/phenylketonuria/symptoms-causes/syc-20376302
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Sickle cell anemia [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sickle-cell-anemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20355876
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Turner syndrome [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/turner-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20360782
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Triple X syndrome [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/triple-x-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20350977
National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities. (2020). Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs): Basics about FASDs [webpage]. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/fasd/facts.html
TED-Ed. (2019, January 24). How CRISPR lets you edit DNA – Andrea M. Henle. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6tw_JVz_IEc
TED. (2016, October 24). What you need to know about CRISPR | Ellen Jorgensen. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1BXYSGepx7Q&feature=youtu.be
TED. (2017, February 10). The ethical dilemma of designer babies | Paul Knoepfler. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nOHbn8Q1fBM&t=3s
Diseases, syndromes, or other abnormal conditions caused by mutations in one or more genes, or by chromosomal alterations.
An alteration in the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism.
A medical condition that is present at or before birth. These conditions, also referred to as birth defects, can be acquired during the fetal stage of development or from the genetic make up of the parents.
Refers to the relationship between two versions of a gene. Individuals receive two versions of each gene, known as alleles, from each parent. If the alleles of a gene are different, one allele will be expressed; it is the dominant gene. The effect of the other allele, called recessive, is masked.
A person or other organism that has inherited a recessive allele for a genetic trait or mutation but usually does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease.
A special type of cell division in sexually-reproducing organisms used to produce the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome.
The failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division.
A threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
A mature haploid male or female germ cell which is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote.
The union of the sperm cell and the egg cell. Also known as a fertilized ovum, the zygote begins as a single cell but divides rapidly in the days following fertilization. After this two-week period of cell division, the zygote eventually becomes an embryo.
A medical procedure used primarily in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and fetal infections as well as for sex determination. In this procedure, a small amount of amniotic fluid, which contains fetal tissues, is sampled from the amniotic sac surrounding a developing fetus.
Biological molecules that lower amount the energy required for a reaction to occur.
An experimental technique that uses genes to treat or prevent disease.
A sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA that codes for a molecule that has a function.
The smallest unit of life, consisting of at least a membrane, cytoplasm, and genetic material.
A class of biological molecule consisting of linked monomers of amino acids and which are the most versatile macromolecules in living systems and serve crucial functions in essentially all biological processes.
A carrier genetically engineered to deliver a gene. Certain viruses are often used as vectors because they can deliver the new gene by infecting the cell.

