157 18.6 Structures of the Female Reproductive System
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller

Fertility Symbol
The geometric design on the ancient stone carving in Figure 18.6.1 represents a powerful symbol of female fertility: the vagina. The symbol is called yoni in Hindu, and it reflects the value placed by Hindu culture on the ability of females to give birth. The vagina is one of several organs in the female reproductive system.
Female Reproductive Organs
The female reproductive system is made up of internal and external organs that function to produce haploid female gametes called ova (or oocytes), secrete female sex hormones (such as estrogen), and carry and give birth to a fetus. The internal female reproductive organs include the vagina, uterus, oviducts, and ovaries. The external organs — collectively called the vulva — include the clitoris and labia.
The vagina is an elastic, muscular canal leading from its opening in the vulva to the neck of the uterus, called the cervix. It is about 7.5 cm (about 3 in) long at the front, and about 9 cm (3.5 in) long at the back. The vagina accommodates the penis and is the site where sperm are usually ejaculated during sexual intercourse. In the context of pregnancy and natural (vaginal) childbirth, the vagina is referred to as the birth canal. In addition, it channels the flow of menstrual blood from the uterus.
Structure of the Vagina
Muscles and ligaments support the vagina within the pelvic cavity. The vagina itself is made up of several layers of fibrous and muscular tissues and lined with mucous membranes. Folds in the mucosa provide the vagina with extra surface area so it can stretch in both length and width during intercourse or childbirth. The elasticity of the vagina and the extra mucosa allow it to stretch to many times its normal diameter in order to deliver a baby.
Bacteria and pH in the Vagina
A healthy vagina is home to many symbiotic bacteria that help prevent pathogens (such as yeast) from colonizing the vagina. The pH in the vagina is normally between 3.8 and 4.5, and this acidity also helps keep pathogenic microorganisms from colonizing it. The vagina constantly sheds its epithelium, so it is considered self-cleaning. As a consequence, there is no need for douching to clean it. Physicians actually discourage the practice, as it may upset the normal bacterial and pH balance in the vagina, although washing the vulva with a mild soap is good practice.
Uterus
The uterus (commonly called the womb) is a pear-shaped, muscular organ that is about 7.6 cm (about 3 in) long. It is located above the vagina and behind the bladder in the centre of the pelvis. The position of the uterus in the pelvis is stabilized by several ligaments and bands of supportive tissue. The uterus is where a fetus develops during gestation, and the organ provides mechanical protection and support for the developing offspring. Contractions of the muscular wall of the uterus are responsible for pushing the fetus out of the uterus during childbirth.
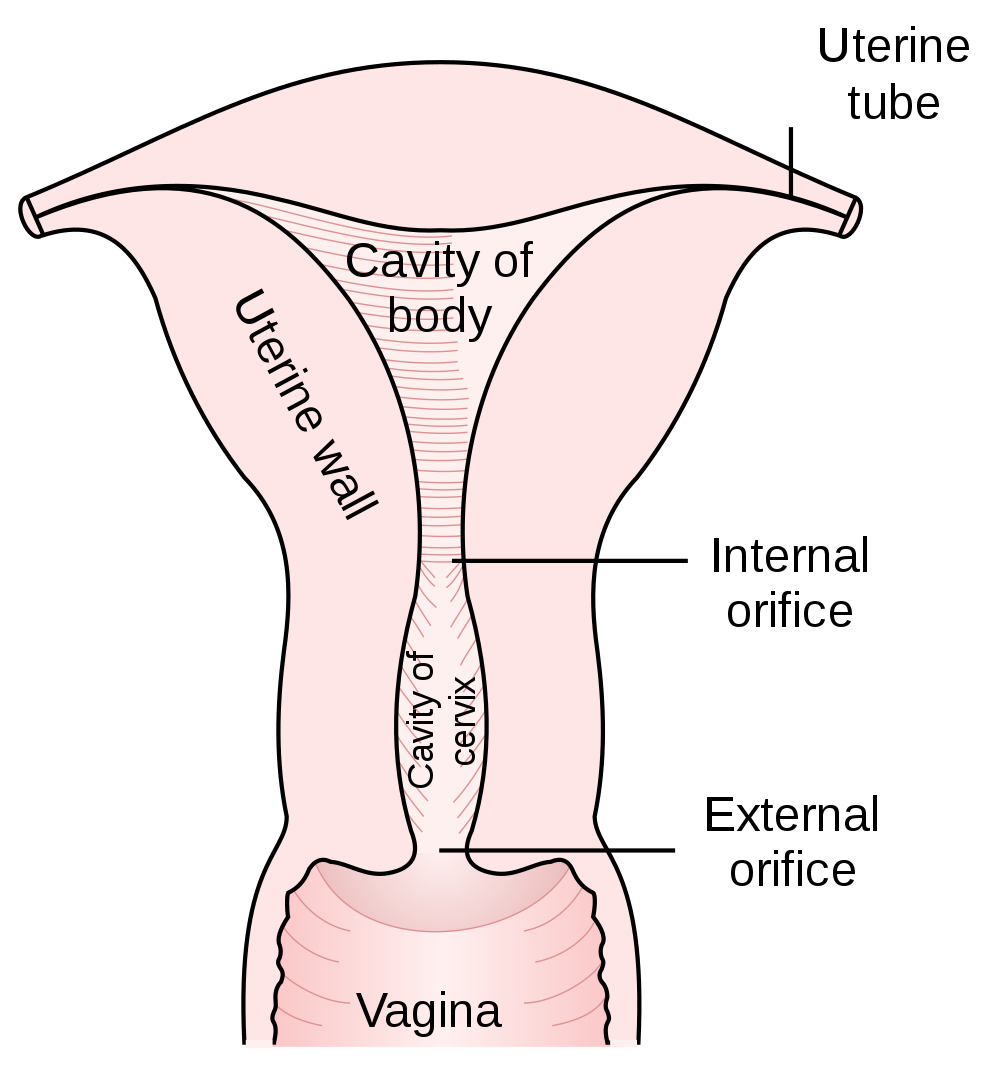
Parts of the Uterus
As shown in Figure 18.6.2, the lower end of the uterus forms the cervix, which is also called the neck of the uterus. The cervix is about 2.5 cm (almost 1 in) long and protrudes downward into the vagina. A small canal runs the length of the cervix, connecting the uterine cavity with the lumen of the vagina. This allows semen deposited in the vagina to enter the uterus, and a baby to pass from the uterus into the vagina during birth. Glands in the cervix secrete mucus that varies in water content and thickness, so it can function either as a barrier to keep microorganisms out of the uterus during pregnancy, or as a transport medium to help sperm enter the uterus around the time of ovulation. The rest of the uterus above the cervix is called the body of the uterus. The upper end of the uterus is connected with the two oviducts.
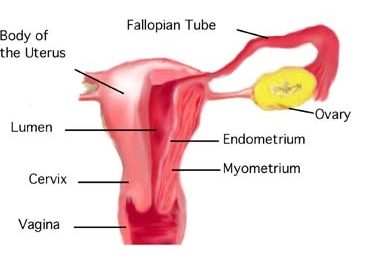
Tissues of the Uterus
As indicated in Figure 18.6.3, the uterus consists of three tissue layers, called the endometrium, myometrium, and perimetrium.
- The endometrium is the innermost tissue layer of the uterus. It consists of epithelial tissue, including mucous membranes. This layer thickens during each menstrual cycle and, unless an egg is fertilized, sloughs off during the following menstrual period. If an ovum is fertilized, the thickened endometrium is maintained by hormones and provides nourishment to the embryo. As gestation progresses, the endometrium develops into the maternal portion of the placenta.
- The placenta is a temporary organ that consists of a mass of maternal and fetal blood vessels through which the mother’s and fetus’s blood exchange substances.
- The myometrium is the middle layer of the uterus. It consists mostly of a thick layer of smooth muscle tissue. Powerful contractions of the smooth muscle allow the uterus to contract and expel an infant during childbirth.
- The perimetrium is the outermost layer of the uterus. It covers the outer surface of the uterus. This layer actually consists of two layers of epithelium that secrete fluid into the space between them. The fluid allows for small movements of the uterus within the pelvis, without causing it to rub against other organs.
Oviducts
The oviducts (often referred to as Fallopian tubes) are two thin tubes that lie between the ovaries and the uterus. The oviducts are not attached to the ovaries, but their broad upper ends — called infundibula — lie very close to the ovaries. The infundibula also have fringe-like extensions called fimbriae that move in a waving motion to help guide eggs from the ovaries into the oviducts. The lower ends of the oviducts are attached to the upper part of the body of the uterus on either side of the body. They open into the uterus.
The oviducts are made up of multiple tissue layers. The innermost layer consists of mucosal epithelium. The epithelium is covered with cilia, which can move in a sweeping motion to help ova move through the tube from the ovary to the uterus. In between the ciliated cells of the epithelium are cells that secrete a fluid called tubular fluid. This fluid contains nutrients for sperm, ova, and zygotes. The secretions in tubular fluid also remove certain molecules from the plasma membrane of sperm so they are better able to penetrate an egg. Other layers of the oviducts consist of connective tissue and smooth muscle. Contractions of the smooth muscle allow peristalsis to help move eggs through the tubes.
Ovaries
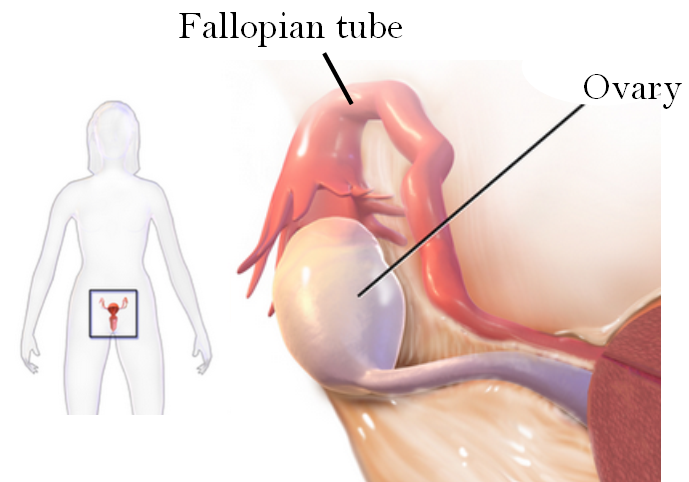
Like the testes in males, the ovaries in females are gonads that produce gametes and secrete sex hormones. The gametes produced by the ovaries are called ova, or oocytes. The main sex hormone secreted by the ovaries is estrogen. The position of the paired ovaries relative to the other reproductive system organs is shown in Figure 18.6.4. Each ovary lies along one side of the uterus and is about 4 cm (a little more than 1.5 in) long. Fibrous ligaments attach one end of each ovary to its nearby oviduct and the other and to its side of the uterus. These ligaments keep the ovaries in place within the pelvis.
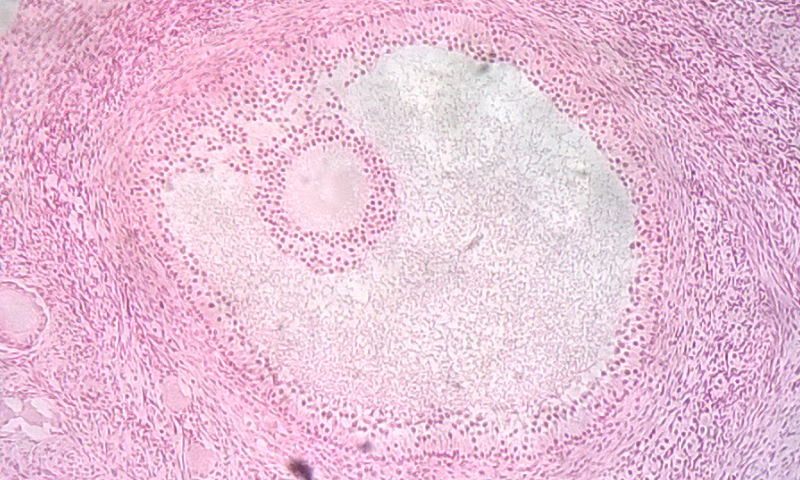
Ovarian Follicles
The ovary consists of two main layers, called the ovarian medulla (the inner layer) and the ovarian cortex (the outer layer). The ovary also contains blood and lymphatic vessels. The ovarian cortex consists primarily of the functional units of the ovaries, which are called ovarian follicles. The follicles are nests of epithelial cells, within each of which is an ovum. The photomicrograph in Figure 18.6.5 shows an ovarian follicle and the developing ovum inside it. If an ovum and follicle complete maturation, the follicle ruptures and the ovum is released from the ovary. This event is called ovulation.
Ova in the Ovaries
Whereas the male testes produce sperm continuously after puberty, the female ovary already contains all the ova it will ever produce by the time a female is born. At birth, a baby girl’s ovaries contain at least a million eggs, each of which is contained within a follicle. Only about 500 of these eggs will eventually mature and be ovulated. This process starts at puberty and typically continues at monthly intervals until menopause occurs around age 52. The remaining eggs never mature, and their number declines as the woman ages. By menopause, a woman’s reserve of eggs is nearly depleted, and ovulation no longer occurs.
Vulva
The vulva is a general term for all of the external female reproductive organs. The vulva includes the clitoris, labia, and external openings for the urethra and vagina.
Labia
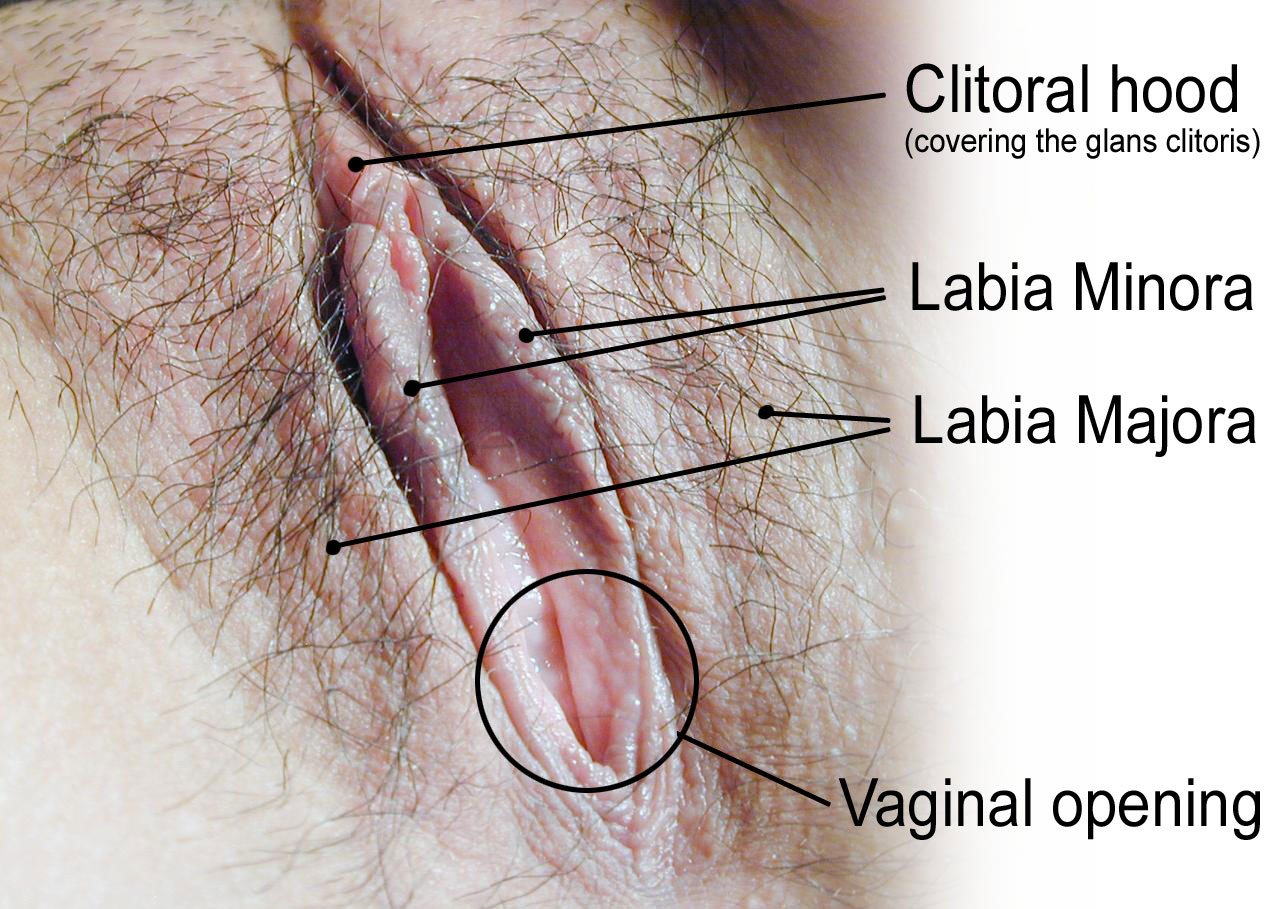
The labia (singular, labium) refer to the “lips” of the vulva, which are folds of tissue that contain and protect the other, more delicate structures of the vulva (as shown in Figure 18.6.6). There are two pairs of labia: the outer and larger labia majora, and the inner and smaller labia minora. The labia minora contain numerous sebaceous glands. These glands release secretions that help lubricate the labia and vulvar area.
Clitoris
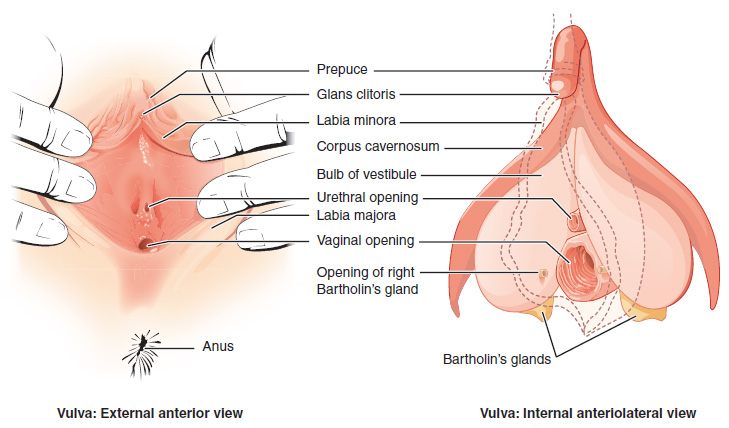
The clitoris, is located at the front of the vulva where the labia minora meet. The visible portion of the clitoris is called the glans clitoris. It is roughly the size and shape of a pea. It is highly sensitive, because it contains many nerve endings. A hood of tissue called the clitoral hood (shown in Figure 18.6.5 above), or prepuce, normally covers and protects the clitoris. The clitoris is the homologue to the male penis, and they both contain spongy tissue. Stimulation of the glans clitoris during sexual activity generally results in sexual arousal in females, and may lead to orgasm. The glans clitoris is the only part of the overall clitoris visible externally, but this spongy tissue extends down either side of the openings to the urethra and vagina, as seen in Figure 18.6.7.
Other Vulvar Structures
The area between the two labia minora is called the vestibule of the vulva. Both the urethra and vagina have openings to the outside of the body in the vestibule. As you can see in Figure 18.6.7 above, the urethral opening (or meatus) is located just in front of, and is much smaller than, the vaginal opening. Both openings are protected by the labia. Two glands — called Bartholin’s glands — open on either side of the vaginal opening. These glands secrete mucus and a vaginal and vulvar lubricant.
Breasts
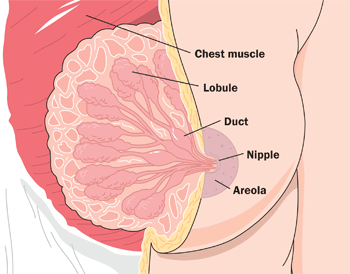
The breasts are not directly involved in reproduction, but because they contain mammary glands, they can provide nourishment to an infant after birth. The breasts overlay major muscles in the chest from which they project outward in a conical shape. The two main types of tissues in the breast are adipose (fat) tissue and glandular tissue that produces milk. As shown in Figure 18.6.8, each mature breast contains many lobules, where milk is produced and stored during pregnancy. During breastfeeding (or lactation), the milk drains into ducts and sacs, which in turn converge at the nipple. Milk exits the breast through the nipple in response to the suckling action of an infant and is regulated by a positive feedback loop. The nipple is surrounded by a more darkly pigmented area called the areola. The areola contains glands that secrete an oily fluid, which lubricates and protects the nipple during breastfeeding.
18.6 Summary
- The female reproductive system is made up of internal and external organs that function to produce haploid female gametes called ova, secrete female sex hormones (such as estrogen), and carry and give birth to a fetus.
- The vagina is an elastic, muscular canal that can accommodate the penis. It is also where sperm are usually ejaculated during sexual intercourse. The vagina is the birth canal, and it channels the flow of menstrual blood from the uterus. A healthy vagina has a balance of symbiotic bacteria and an acidic pH.
- The uterus is a muscular organ above the vagina where a fetus develops. Its muscular walls contract to push out the fetus during childbirth. The cervix is the neck of the uterus that extends down into the vagina. It contains a canal connecting the vagina and uterus for sperm, or for an infant to pass through. The innermost layer of the uterus — the endometrium — thickens each month in preparation for an embryo, but is shed in the following menstrual period if fertilization does not occur.
- The oviducts extend from the uterus to the ovaries. Waving fimbriae at the ovary ends of the oviducts guide ovulated eggs into the tubes where fertilization may occur as the ova travel to the uterus. Cilia and peristalsis help ova move through the tubes. Tubular fluid helps nourish sperm as they swim up the tubes toward ova.
- The ovaries are gonads that produce ova and secrete sex hormones, including estrogen. Nests of cells called follicles in the ovarian cortex are the functional units of ovaries. Each follicle surrounds an immature ovum. At birth, a baby girl’s ovaries contain at least a million ova, and they will not produce any more during her lifetime. During a woman’s reproductive years, one ova typically matures and is ovulated each month.
- The vulva is a general term for external female reproductive organs. The vulva includes the clitoris, two pairs of labia, and openings for the urethra and vagina. Secretions from mucosal glands near the vaginal opening lubricate the vulva.
- The breasts are not technically reproductive organs, but their mammary glands produce milk to feed an infant after birth. Milk drains through ducts and sacs, and out through the nipple when a baby sucks during breastfeeding.
18.6 Review Questions
-
- State the general functions of the female reproductive system.
- Describe the vagina and its reproductive functions.
- Outline the structure and basic functions of the uterus.
- What is the endometrium? How does it change during the monthly cycle?
- Why are breasts included in discussions of reproduction, if they are not organs of the female reproductive system?
- What is the function of the folds in the mucous membrane lining of the vagina?
- What are two ways in which the female reproductive system protects itself from pathogens?
18.6 Explore More
The uncomplicated truth about women’s sexuality | Sarah Barmak, TED, 2019.
Human Physiology – Functional Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System, Janux, 2015.
Attributes
Figure 18.6.1
1024px-Cattien_stone_yoni by Binh Giang on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/en:public_domain).
Figure 18.6.2
1000px-Gray1167.svg by Henry Vandyke Carter (1831-1897) on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/public_domain). (Bartleby.com: Gray’s Anatomy, Plate 1167).
Figure 18.6.3
Uterine_anatomy. from Uterine Stem cells by The Stem Cell Research Community, StemBook on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
Figure 18.6.4
Sites_of_tubo_ovarian_abscess by Bfpage on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 18.6.5
Ovarian_follicle by TiagoLubiana on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 18.6.6
HumanVulva-NewText-PhiloViv by Amphis (edited) on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en) license. (Original en:Image:HumanVulva-NoText-PhiloVivero.jpg by en:user:PhiloVivero)
Figure 18.6.7
Vulva by OpenStax College on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
Figure 18.6.8
Breast-Diagram by Women’s Health (NCI/ NIH) on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/en:Public_domain).
References
Betts, J. G., Young, K.A., Wise, J.A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Kruse, D.H., Korol, O., Johnson, J.E., Womble, M., DeSaix, P. (2013, June 19). Figure 27.10 The vulva [digital image]. In Anatomy and Physiology (Section 27.2). OpenStax. https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/27-2-anatomy-and-physiology-of-the-female-reproductive-system
Janux. (2015, January 10). Human physiology – Functional anatomy of the female reproductive system. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9rs2gNchQig&feature=youtu.be
TED. (2019, March 22). The uncomplicated truth about women’s sexuality | Sarah Barmak. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SkB4gG8ke7Q&feature=youtu.be
Teixeira, J., Rueda, B.R., and Pru, J.K. (September 30, 2008). Figure 1 Uterine anatomy. In Uterine Stem Cells (StemBook, ed.). The Stem Cell Research Community, StemBook, doi/10.3824/stembook.1.16.1, http://www.stembook.org
The female reproductive organ that receives sperm during sexual intercourse and provides a passageway for a baby to leave the mother’s body during birth.
The female sex hormone secreted mainly by the ovaries.
An unborn offspring of a mammal, in particular an unborn human baby more than eight weeks after conception.
The female reproductive organ in which first an embryo and then a fetus grows and develops until birth.
One of two female reproductive organs that carry eggs from an ovary to the uterus and are the site where fertilization usually takes place.
A pair of female reproductive organs that produces eggs and secretes estrogen.
External female reproductive structures, including the clitoris, labia, and vaginal and urethral openings.
The small, sensitive external female organ that is part of the vulva and may lead to sexual arousal and/or orgasm when stimulated.
The “lips” of the vulva, consisting of folds of tissue that protect the urethral and vaginal openings.
The neck of the uterus that protrudes down into the vagina and through which a canal connects the vagina and uterus.
The male reproductive cell.
A body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet (the superior opening of the pelvis). Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor. The pelvic cavity primarily contains reproductive organs, the urinary bladder, the pelvic colon, and the rectum.
Epithelial tissue that lines inner body surfaces and body openings and produces mucus.
Any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms.
Any member of a large group of unicellular microorganisms which have cell walls but lack organelles and an organized nucleus, including some which can cause disease.
A measure of the acidity or basicity of aqueous or other liquid solutions. The term translates the values of the concentration of the hydrogen ion in a scale ranging from 0 and 14. In pure water, which is neutral (neither acidic nor alkaline), the concentration of the hydrogen ion corresponds to a pH of 7. A solution with a pH less than 7 is considered acidic; a solution with a pH greater than 7 is considered basic, or alkaline.
A sac-like organ that stores urine until it is excreted from the body.
An organisms that is so small it is invisible to the human eye.
The release of a secondary oocyte from an ovary about half way through the menstrual cycle.
The innermost layer of the uterus that builds up during each menstrual cycle and helps nourish the embryo if fertilization occurs or is shed from the uterus as menstrual flow if fertilization does not occur.
A temporary organ that consists of a large mass of maternal and fetal blood vessels through which the mother’s and embryo’s or fetus’s blood exchange substances.
The middle layer of the uterine wall, consisting mainly of uterine smooth muscle cells (also called uterine myocytes) but also of supporting stromal and vascular tissue. Its main function is to induce uterine contractions.
The outer serous layer of the uterus. The serous layer secretes a lubricating fluid that helps to reduce friction.
Small, fingerlike projections at the end of the oviducts, through which eggs move from the ovaries to the uterus. The fimbriae are connected to the ovary.
Tiny hairlike organelles, identical in structure to flagella, that line the surfaces of certain cells and beat in rhythmic waves, providing locomotion to ciliate protozoans and moving liquids along internal epithelial tissue in animals.
A semi-permeable lipid bilayer that separates the interior of all cells from their surroundings.
An involuntary, nonstriated muscle that is found in the walls of internal organs such as the stomach.
A distinctive pattern of smooth muscle contractions that propels foodstuffs distally through the esophagus and intestines.
Two male reproductive organs that produce sperm and secrete testosterone; male gonad.
One of a pair of organs that secrete sex hormones and produce gametes; testis in males and ovary in females.
A mature haploid male or female germ cell which is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote.
A hormone is a signaling molecule produced by glands in multicellular organisms that target distant organs to regulate physiology and behavior.
The gamete produced by a female.
A hollow, tube-like structure through which blood flows in the cardiovascular system; vein, artery, or capillary.
The functional unit of an ovary that consists of a nest of epithelial cells surrounding an egg.
A period during which humans become sexually mature.
The cessation of a woman’s menstrual cycles, usually by age 52.
A tube-like organ of the urinary system that carries urine out of the body from the bladder and, in males, also carries semen out of the body.
An exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word mamma, "breast".
A control mechanism that serves to intensify a response until an endpoint is reached.
The term used when a cell has half the usual number of chromosomes.
The male reproductive organ containing the urethra, through which semen and urine pass out of the body.
The physical activity of sex between two people.
Having a higher proportion of hydronium ions than hydroxide ions; having the properties of an acid; having a pH below 7.
A stage of growth and development that occurs from implantation in the uterus through the eighth week after fertilization.
The fusion of haploid gametes, egg and sperm, to form the diploid zygote.

