129 14.7 Case Study Conclusion: Flight Risk
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller
Case Study Conclusion: Flight Risk
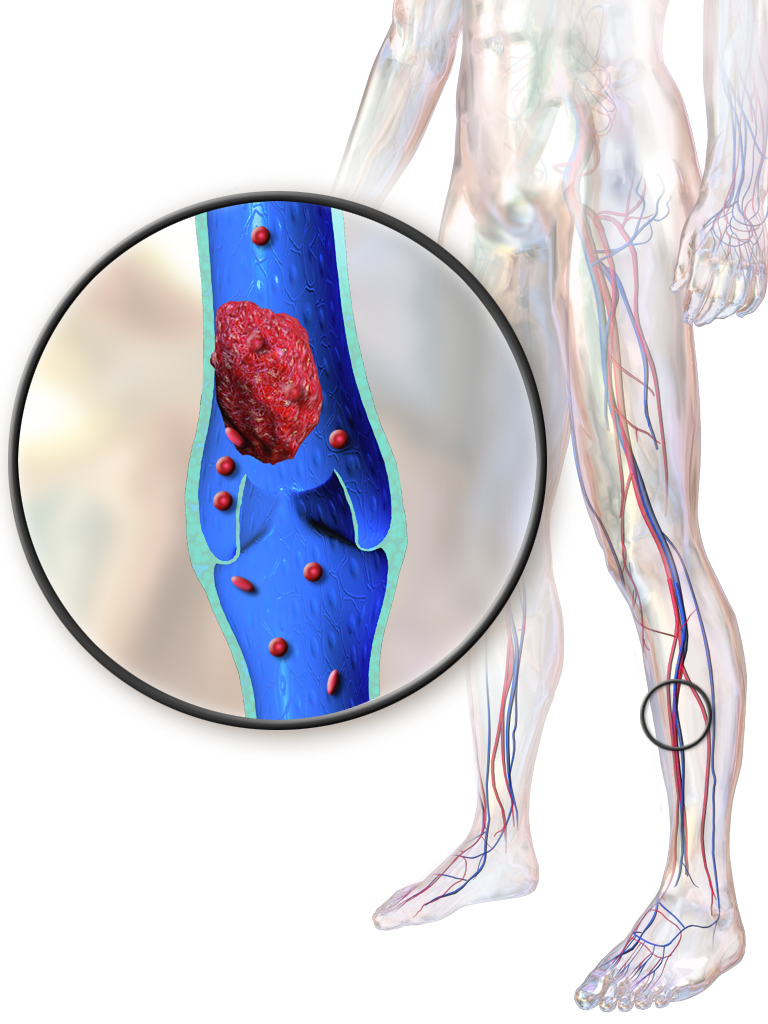
At the beginning of this chapter, you learned about Malcolm and Willie, who met while sitting next to each other on a plane. During the flight, Willie got up to take frequent walks, and was doing leg exercises to try to avoid the medical condition depicted in Figure 14.7.1 — deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg. It can be very dangerous — even deadly.
As you learned in this chapter, a blood clot is an aggregation of thrombocytes and proteins. Blood clots are helpful for preventing blood loss when a blood vessel is damaged. In some situations, though, they can be extremely dangerous. Blood clots can cause heart attacks or strokes by blocking the flow of blood to the heart or brain, respectively.
When DVT occurs, one of the major risks is pulmonary embolism (PE). PE is when the blood clot breaks off, travels through the blood vessels, and lodges in a pulmonary artery. Recall what the pulmonary arteries do — they carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where the blood picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide due to gas exchange between the capillaries and the alveoli of the lungs. Imagine what would happen if this flow of blood to the lungs was partially or completely blocked by a blood clot. Depending on the size of the blood clot and where it is lodged, a PE can cause a variety of serious consequences, ranging from lung damage to instant death, because of the disruption of the pulmonary circulation.
Willie has a higher risk of DVT and its consequences because he has heart failure. As you have learned, heart failure is a chronic condition in which the pumping action of the heart is impaired. One reason that heart failure is thought to increase the risk of DVT is because the blood is not being pushed strongly enough through the cardiovascular system, allowing blood clots to form more easily.
Willie needs to be particularly concerned about DVT while on a long plane flight. Why do you think this is? Think about how blood flows through arteries and veins. Blood is pushed through arteries mainly due to the pumping action of the heart. Veins, on the other hand, rely on the movement of the surrounding skeletal muscles to help push blood through them. Sitting still for long periods of time in cramped quarters (such as on a plane) can cause blood to pool in the deep veins of the legs, leading to the formation of a blood clot.
Even people who are generally healthy and don’t have heart disease can get DVT from sitting for too long on a long-distance flight, or in other situations when they are immobile for extended periods of time. Fortunately, walking periodically and doing some simple leg exercises can lower your risk of DVT by helping to push blood through your veins. If you are planning on taking a flight in the future, watch the short video below to learn some easy exercises that you can do right in your plane seat to help prevent DVT!
Chapter 14 Summary
In this chapter you learned about the structure, functions, and disorders of the cardiovascular system. Specifically, you learned that:
- The cardiovascular system is the organ system that transports materials to and from all the cells of the body. The main components of the cardiovascular system are the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
- The cardiovascular system has two interconnected circulations. The pulmonary circuit carries blood between the heart and lungs, where blood is oxygenated. The systemic circuit carries blood between the heart and the rest of the body, where it delivers oxygen.
- The heart is a muscular organ in the chest that consists mainly of cardiac muscle. It pumps blood through blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions.
-
- The wall of the heart consists of three layers. The middle layer, the myocardium, is the thickest layer, and consists mainly of cardiac muscle.
- The interior of the heart consists of four chambers, with an upper atrium and lower ventricle on each side of the heart. Blood enters the heart through the atria, which pump it to the ventricles. Then, the ventricles pump blood out of the heart. Four valves in the heart keep blood flowing in the correct direction and prevent backflow.
-
- Deoxygenated blood flows into the right atrium through veins from the upper and lower body (superior and inferior vena cava, respectively), and oxygenated blood flows into the left atrium through four pulmonary veins from the lungs. Each atrium pumps the blood to the ventricle below it. From the right ventricle, deoxygenated blood is pumped to the lungs through the two pulmonary arteries. From the left ventricle, oxygenated blood is pumped to the rest of the body through the aorta.
- The coronary circulation consists of blood vessels that carry blood to and from the heart muscle cells. There are two coronary arteries that supply the two sides of the heart with oxygenated blood. Cardiac veins drain deoxygenated blood back into the heart.
- The cardiac cycle refers to a single complete heartbeat. It includes diastole — when the atria contract — and systole, when the ventricles contract.
- The normal, rhythmic beating of the heart is called sinus rhythm. It is established by the heart’s pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node. Electrical signals from the pacemaker cells travel to the atria and cause them to contract. Then, the signals travel to the atrioventricular node, and from there to the ventricles via the Purkinje fibres, causing them to contract. Electrical stimulation from the autonomic nervous system and hormones from the endocrine system can also influence heartbeat.
- Blood vessels carry blood throughout the body. Major types of blood vessels are arteries, veins, and capillaries.
-
- Arteries are blood vessels that usually carry blood away from the heart (except for coronary arteries that supply the heart muscle with blood). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood. The largest artery is the aorta, which is connected to the heart and extends into the abdomen. Blood moves through arteries due to pressure from the beating of the heart.
- Veins are blood vessels that usually carry blood toward the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood. The largest veins are the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. Blood moves through veins by the squeezing action of surrounding skeletal muscles. Valves in veins prevent backflow of blood.
- Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels. They connect arterioles and venules. They form capillary beds where substances are exchanged between the blood and surrounding tissues.
- The walls of arteries and veins have three layers. The middle layer is thickest in arteries, in which it contains smooth muscle tissue that controls the diameter of the vessels. The outer layer is thickest in veins and consists mainly of connective tissue. The walls of capillaries consist of little more than a single layer of epithelial cells.
- Blood pressure is a measure of the force that blood exerts on the walls of arteries. It is expressed as a double number, with the higher number representing systolic pressure when the ventricles contract, and the lower number representing diastolic pressure when the ventricles relax. Normal blood pressure is generally defined as a pressure of 120/80 mm Hg or less.
- Vasoconstriction (narrowing) and vasodilation (widening) of arteries can occur to help regulate blood pressure or body temperature or to change blood flow as part of the fight-or-flight response.
- Blood is a fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body in blood vessels. Blood supplies tissues with oxygen and nutrients, and removes their metabolic wastes. Blood helps defend the body from pathogens and other threats, transports hormones and other substances, and helps to keep the body’s pH and temperature in homeostasis. Blood consists of a liquid part (called plasma) and cells, including erythrocytes, leukocytes and thrombocytes.
-
- Plasma makes up more than half of blood by volume. It consists of water and many dissolved substances. It also contains blood cells.
- Erythrocytes are the most numerous cells in blood. They consist mostly of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen. Red blood cells also carry antigens that determine blood types.
- Leukocytes are less numerous than red blood cells and are part of the body’s immune system. They protect the body from abnormal cells, microorganisms, and other harmful substances. There are several different types of white blood cells that differ in their specific immune functions.
- Thrombocytes are cell fragments that play important roles in blood clotting, or coagulation. They stick together at breaks in blood vessels to form a clot and stimulate the production of fibrin, which strengthens the clot.
- All blood cells form by proliferation of stem cells in red bone marrow in a process called hematopoiesis. When blood cells die, they are phagocytized by white blood cells and removed from the circulation.
- Disorders of the blood include leukemia, which is cancer of the bone-forming cells; hemophilia, which is any of several genetic blood-clotting disorders; carbon monoxide poisoning, which prevents erythrocytes from binding with oxygen and causes suffocation; HIV infection, which destroys certain leukocytes and can cause AIDS; and anemia, in which there are not enough erythrocytes to carry adequate oxygen to body tissues.
- Cardiovascular disease is a class of diseases that involve the cardiovascular system. Worldwide, it is the leading cause of death. Most cases occur in people over age 60, and onset typically occurs about a decade earlier in males than in females. Other risk factors include smoking, obesity, diabetes, high blood cholesterol, and lack of exercise.
-
- Two common conditions that lead to most cases of cardiovascular disease are hypertension and atherosclerosis. Hypertension is blood pressure that is persistently at or above 140/90 mm Hg. Atherosclerosis is a buildup of fatty, fibrous plaques in arteries that may reduce or block blood flow. Treating these conditions is important for preventing cardiovascular disease.
- Coronary artery disease is a group of diseases that result from atherosclerosis of coronary arteries. Two of the most common are angina and myocardial infarction (heart attack). In angina, cardiac cells receive inadequate oxygen, which causes chest pain. In a heart attack, cardiac cells die because blood flow to part of the heart is blocked. A heart attack may cause death, or lead to heart arrhythmias, heart failure, or cardiac arrest.
- Stroke occurs when blocked or broken arteries in the brain result in the death of brain cells. This may happen when an artery is blocked by a clot or plaque, or when an artery ruptures and bleeds in the brain. In both cases, part of the brain is damaged, and functions such as speech and controlled movements may be impaired, either temporarily or permanently.
- Peripheral artery disease occurs when atherosclerosis narrows peripheral arteries, usually in the legs, often causing pain when walking. It is important to diagnose this disease so the underlying atherosclerosis can be treated before it causes a heart attack or stroke.
In this chapter, you learned that the cardiovascular system carries nutrients to the cells of the body. Read the next chapter about the Digestive System to learn about how your body transforms your meals into the nutrients that cells need to function.
Chapter 14 Review Questions
-
- Alex goes to the doctor and learns that his blood pressure is 135/90 mm Hg. Answer the following questions about his blood pressure:
- Is this a normal blood pressure? Why or why not?
- Which number refers to the systolic pressure? Which number refers to the diastolic pressure?
- Describe what the atria and ventricles of Alex’s heart are doing when the pressure is at 135 mm Hg.
- Alex’s doctor would like him to lower his blood pressure. Why do you think he would like Alex to do this, and what are some ways in which he may be able to lower his blood pressure?
- What are three functions of the cardiovascular system?
- Which are the chambers of the heart that receive blood? Which are the chambers of the heart that pump
- Valves prevent blood from flowing backward in the cardiovascular system. Why do you think this is important?
- Compare the coronary arteries, pulmonary arteries, and arteries elsewhere in the body in terms of their target tissues (i.e. where they bring blood to) and whether they are carrying oxygenated or deoxygenated blood.
- Due to a reduction in the amount of oxygen that gets to the cells of the body, anemia causes weakness and fatigue. Explain how oxygen is transported to the cells of the body, and which blood cells are affected in anemia.
- What are the two conditions that are precursors to virtually all cases of cardiovascular disease?
- What are the main differences between the coronary circulation, pulmonary circulation, and systemic circulation?
- Define sinus rhythm.
- Generally speaking, which is a more serious and immediately life-threatening condition: heart failure or cardiac arrest? Explain your answer.
Attribution
Figure 14.7.1
Blausen_0290_DeepVeinThrombosis by BruceBlaus on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
Reference
Blausen.com Staff. (2014). Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436.
A condition which occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling, but also can occur with no symptoms. It is a particular hazard of long-haul flying.
A blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in your lungs. In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from deep veins in the legs or, rarely, from veins in other parts of the body (deep vein thrombosis).
Refers to the body system consisting of the heart, blood vessels and the blood. Blood contains oxygen and other nutrients which your body needs to survive. The body takes these essential nutrients from the blood.
The part of the cardiovascular system that carries blood between the heart and lungs.
The part of the cardiovascular system that carries blood between the heart and body.
A muscular organ in the chest that pumps blood through blood vessels when it contracts.
Involuntary, striated muscle found only in the walls of the heart; also called myocardium.
A body fluid in humans and other animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. In vertebrates, it is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma.
A hollow, tube-like structure through which blood flows in the cardiovascular system; vein, artery, or capillary.
The muscular tissue of the heart.
One of the two upper chambers of the heart that pumps blood to the ventricle below it. Plural form is atria.
One of two lower chambers of the heart that pumps blood out of the heart.
A large vein carrying deoxygenated blood into the heart. There are two in humans, the inferior vena cava (carrying blood from the lower body) and the superior vena cava (carrying blood from the head, arms, and upper body).
The artery carrying blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
The main artery of the body, supplying oxygenated blood to the circulatory system. In humans it passes over the heart from the left ventricle and runs down in front of the backbone.
One of two arteries that supply the cells of the heart with oxygen and nutrients.
The performance of the human heart from the ending of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following a period of robust contraction and pumping of blood, dubbed systole.
A part of a heartbeat (cardiac cycle) in which the atria contract and pump blood into the ventricles, while the ventricles relax and fill with blood from the atria.
The part of a heartbeat in which the atria relax and fill with blood from the lungs and body, while the ventricles contract and pump blood out of the heart.
The normal, rhythmical beating of the heart.
A small body of specialized muscle tissue in the wall of the right atrium of the heart that acts as a pacemaker by producing a contractile signal at regular intervals.
A part of the electrical conduction system of the heart that coordinates the top of the heart. It electrically connects the atria and ventricles.
division of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary activities
A hormone is a signaling molecule produced by glands in multicellular organisms that target distant organs to regulate physiology and behavior.
The body system which acts as a chemical messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland and the adrenal glands.
A type of blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart and toward the lungs or body.
A type of blood vessel that carries blood toward the heart from the lungs or body.
The smallest type of blood vessel that connects arterioles and venules and that transfers substances between blood and tissues.
An involuntary, nonstriated muscle that is found in the walls of internal organs such as the stomach.
The measure of the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of arteries.
A narrowing of blood vessels so less blood can flow through them.
The widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasoconstriction, which is the narrowing of blood vessels.
An involuntary human body response mediated by the nervous and endocrine systems that prepares the body to fight or flee from perceived danger.
A red blood cell that (in humans) is typically a biconcave disc without a nucleus. Erythrocytes contain the pigment hemoglobin, which imparts the red color to blood, and transport oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from the tissues.
a colorless cell that circulates in the blood and body fluids and is involved in counteracting foreign substances and disease; a white (blood) cell. There are several types, all amoeboid cells with a nucleus, including lymphocytes, granulocytes, monocytes, and macrophages.
Another term for platelet; a small colorless disk-shaped cell fragment without a nucleus, found in large numbers in blood and involved in clotting.
The process in which red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are produced by red bone marrow.
A group of cancers of the blood-forming tissues in bone marrow.
A group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body.
Any of several genetic disorders that cause dysfunction in the blood-clotting process, leading to uncontrolled bleeding from even minor injuries.
Occurs when carbon monoxide builds up in your bloodstream. When too much carbon monoxide is in the air, your body replaces the oxygen in your red blood cells with carbon monoxide. This can lead to serious tissue damage, or even death.
Either of two species of Lentivirus that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive.
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome - a chronic, potentially life-threatening condition caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). By damaging your immune system, HIV interferes with your body's ability to fight infection and disease.
A condition in which you don't have enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to the body's tissues resulting in symptoms including weakness and fatigue.
A class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels.
Abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health. Obesity has been more precisely defined by the National Institutes of Health (the NIH) as a BMI (Body Mass Index) of 30 and above.
A disease caused by problems with the pancreatic hormone insulin, which leads to high blood glucose levels and symptoms such as excessive thirst and urination; includes type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
A persistently high blood pressure, generally defined as 140/90 mm Hg or higher.
A condition in which plaque builds up inside arteries, eventually causing the lumen inside to narrow and the arterial walls to stiffen.
The chest pain or pressure that occurs when heart muscle cells do not receive adequate blood flow and become starved of oxygen.
The blockage of blood flow to heart muscle tissues that may result in the death of cardiac muscle fibers.
A condition in which the heart beats with an irregular or abnormal rhythm.
A cerebrovascular accident in which a broken artery or blood clot results in lack of blood flow to part of the brain, causing death of brain cells.

