91 9.6 Adrenal Glands
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller

Eek!
Being bitten on the nose by an eel certainly qualifies as a frightening experience! The fear this man is experiencing produces the same physiological responses in most people — racing heart, rapid breathing, clammy hands. These and other fight-or-flight responses prepare the body to either defend itself or run away from danger. Why does fear elicit these changes in the body? The responses occur in large part because of hormones secreted by the adrenal glands.
Introduction to the Adrenal Glands
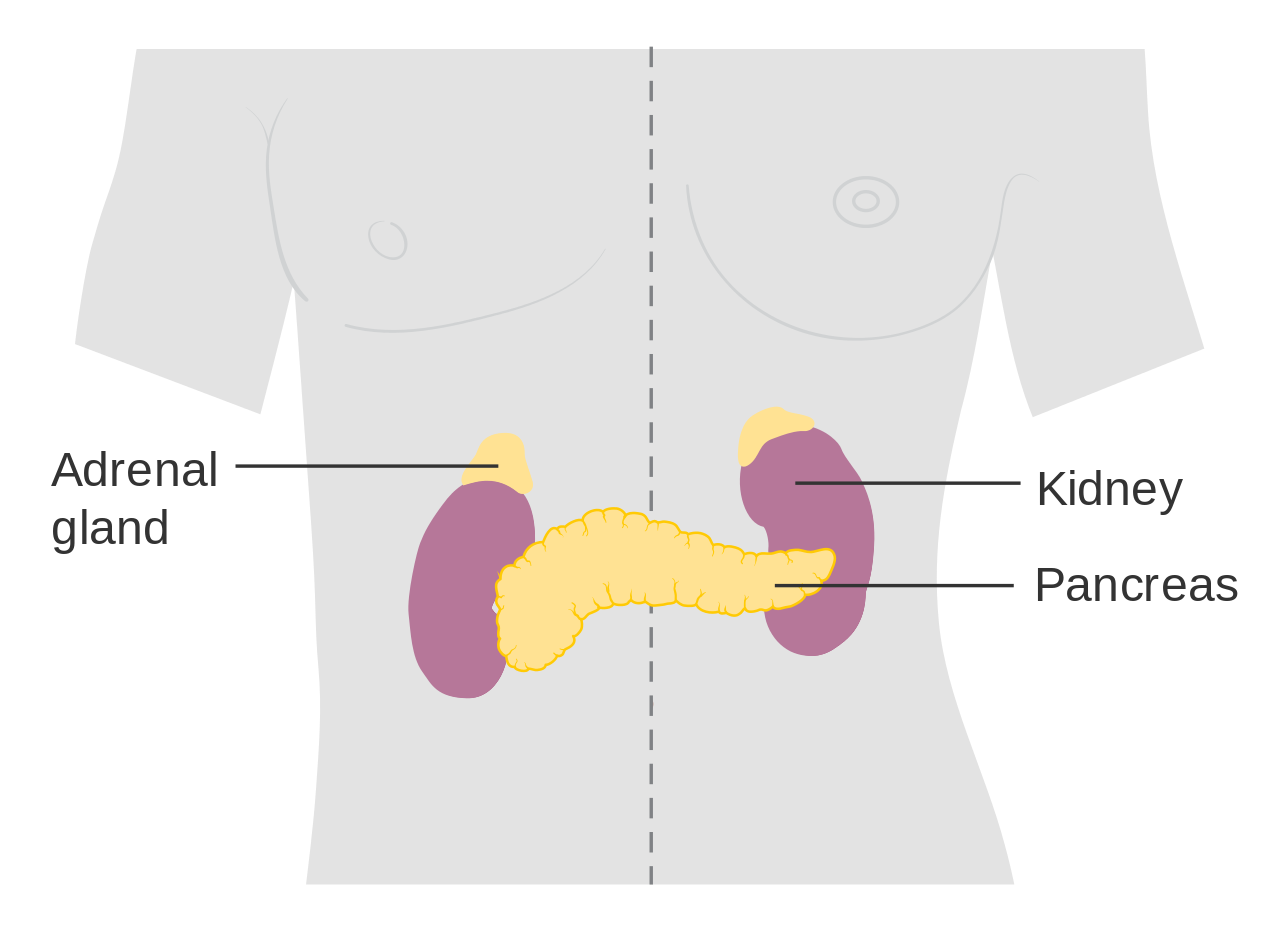
The adrenal glands are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones. Adrenal hormones include the fight-or-flight hormone adrenaline and the steroid hormone cortisol. The two adrenal glands are located on both sides of the body, just above the kidneys, as shown in Figure 9.6.2. The right adrenal gland (on the left in the figure) is smaller and has a pyramidal shape. The left adrenal gland (on the right in the figure) is larger and has a half-moon shape.
Each adrenal gland has two distinct parts, and each part has a different function, although both parts produce hormones. There is an outer layer, called the adrenal cortex, which produces steroid hormones including cortisol. There is also an inner layer, called the adrenal medulla, which produces non-steroid hormones including adrenaline.
Adrenal Cortex
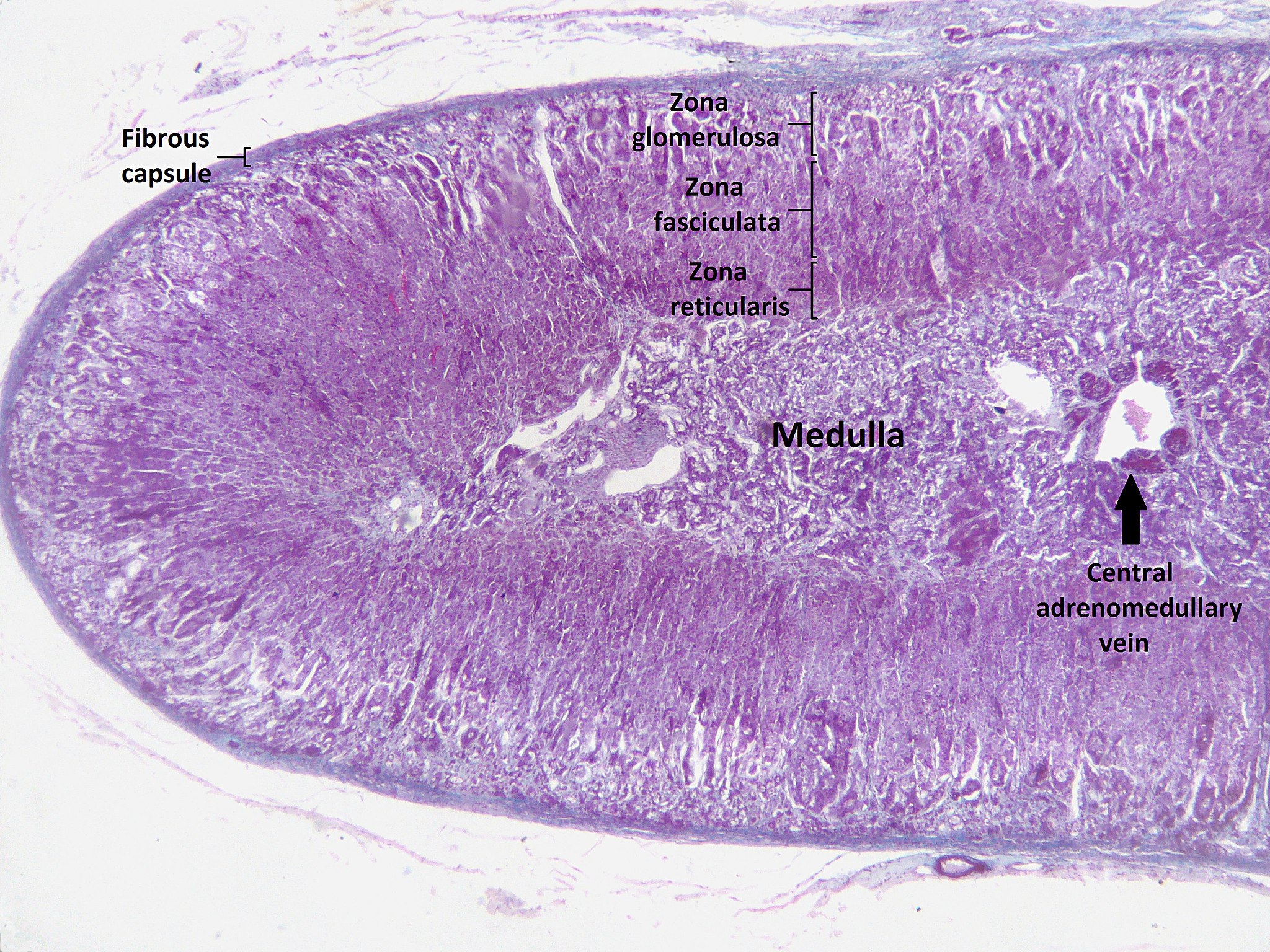
The adrenal cortex, or outer layer of the adrenal gland, is divided into three additional layers, called zones (see Figure 9.6.3). Each zone has distinct enzymes that produce different hormones from the common precursor molecule cholesterol, which is a lipid.
- Zona glomerulosa is the outermost layer of the adrenal cortex. It lies immediately under the outer fibrous capsule that encloses the adrenal gland.
- Zona fasciculata is the middle layer of the adrenal cortex. It is the largest of the three zones, accounting for nearly 80 per cent of the adrenal cortex.
- Zona reticularis is the innermost layer of the adrenal cortex. It is directly adjacent to the medulla of the adrenal gland.
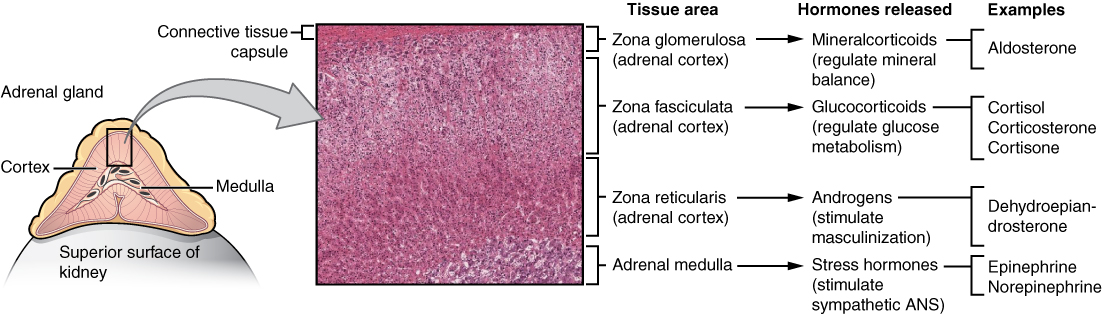
Types of Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Hormones produced by the adrenal cortex are known by the general term corticosteroids. As steroid hormones, corticosteroids are endocrine hormones that are made of lipids and exert their effects on target cells by crossing the plasma membrane and binding with receptors within the cytoplasm. A steroid hormone and its receptor form a complex that enters the cell nucleus and affects gene expression. There are three types of corticosteroids synthesized and secreted by the adrenal cortex. Each type is produced by a different zone of the adrenal cortex, as shown in Figure 9.6.4.
Mineralocorticoids
Mineralocorticoids are produced in the zona glomerulosa and include the hormone aldosterone. These hormones help control the balance of mineral salts (electrolytes) in the body. In the kidneys, aldosterone increases the reabsorption of sodium ions and the excretion of potassium ions. Aldosterone also stimulates the retention of sodium ions by cells in the colon and by the sweat glands. The amount of sodium in the body affects the volume of extracellular fluids (including the blood) and thereby affects blood pressure. In this way, mineralocorticoids help control blood volume and blood pressure.
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids are produced in the zona fasciculata and include the hormone cortisol, which is released in repsonse to stress and is considered the primary stress hormone. Glucocorticoids help control the rate of metabolism of proteins, fats, and sugars. In general, they increase the level of glucose and fatty acids circulating in the blood. Cells rely primarily on glucose for energy, but they can also use fatty acids for energy as an alternative to glucose. Glucocorticoids are also involved in suppression of the immune system, having a potent anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, cortisol reduces the production of new bone and decreases absorption of calcium from the gastrointestinal tract.
Androgens
Androgens are produced in the zona reticularis and include the hormone DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone). Androgens are a general term for male sex hormones, although this is somewhat misleading, as adrenal cortex androgens are produced by both males and females. In adult males, they are converted to more potent androgens, such as testosterone in the male gonads (testes). In adult females, they are converted to female sex hormones called estrogens in the female gonads (ovaries).
Regulation of Adrenal Cortex Hormones
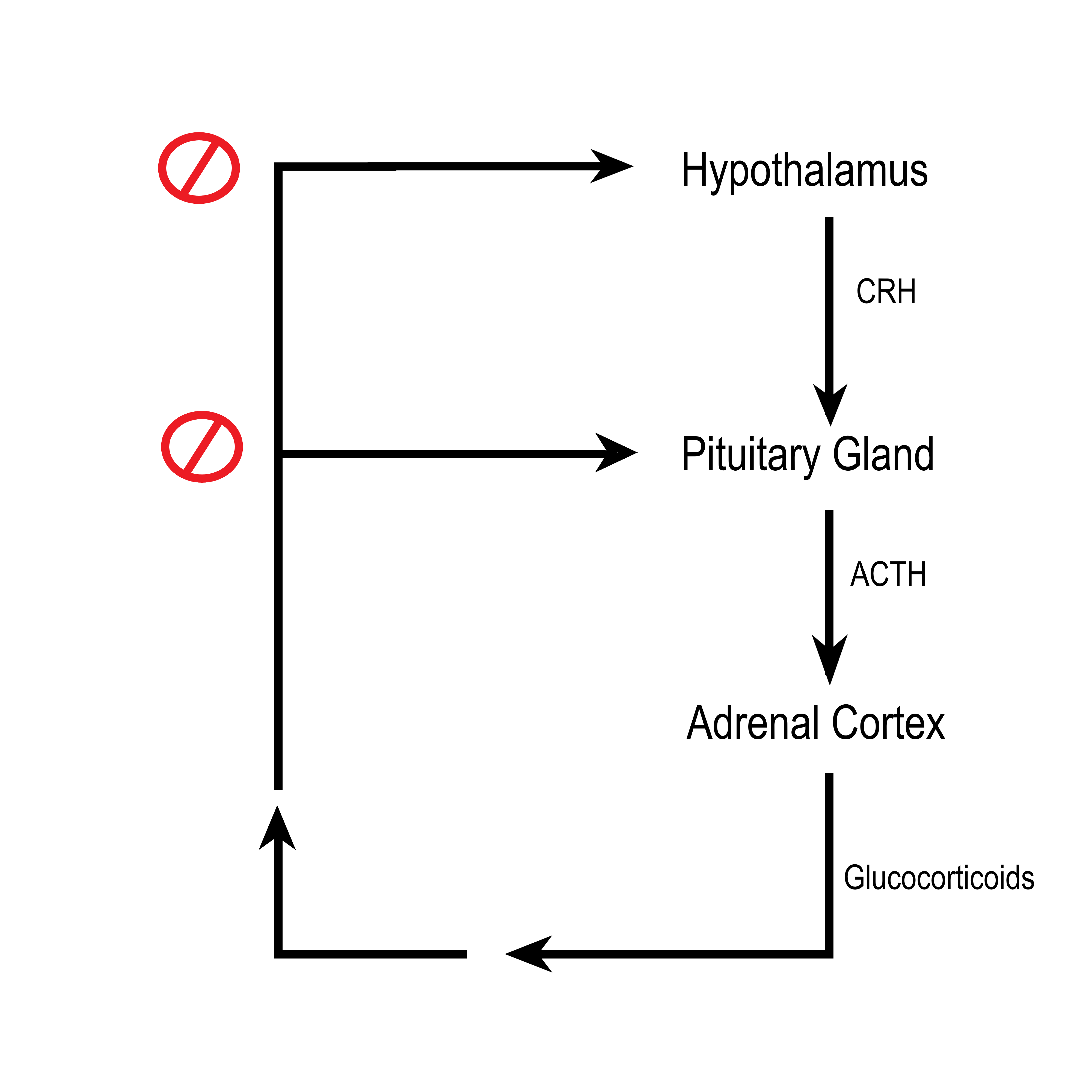
Steroid hormone production by the three zones of the adrenal cortex is regulated by hormones secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, as well as by other physiological stimuli. For example, the production of glucocorticoids such as cortisol is stimulated by adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary, which in turn is stimulated by corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus. When levels of glucocorticoids start to rise too high, they provide negative feedback to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland to stop secreting CRH and ACTH, respectively. This negative feedback mechanism is illustrated in Figure 9.6.5. The opposite occurs when levels of glucocorticoids start to fall too low.
Adrenal Medulla
The adrenal medulla is at the center of each adrenal gland and is surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It contains a dense network of blood vessels into which it secretes its hormones. The hormones synthesized and secreted by the adrenal medulla are generally known as catecholamines, and they include adrenaline (also called epinephrine) and noradrenaline (also called norepinephrine). These water-soluble, non-steroid hormones are made of amino acids. As non-steroid hormones, they cannot cross the plasma membrane of target cells. Instead, they exert their effects by binding to receptors on the surface of target cells. The binding of hormone and receptor activates an enzyme in the plasma membrane that controls a second messenger. It is the second messenger that influences processes inside the cell.
Catecholamines function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stressful situations. They bring about such changes as increased heart rate, more rapid breathing, constriction of blood vessels in certain parts of the body, and an increase in blood pressure. The release of catecholamines by the adrenal medulla is stimulated by activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
Disorders of the Adrenal Glands
Disorders of the adrenal glands generally include either hypersecretion or hyposecretion of adrenal hormones. The underlying cause of the abnormal secretion may be a problem with the adrenal glands or with the pituitary gland, which controls adrenal cortex hormone production. Both adrenal and pituitary glands are subject to the formation of tumors, which may cause adrenal disorders. The adrenal gland may also be affected by infections or autoimmune diseases.
Adrenal Hypersecretion: Cushing’s Syndrome
Hypersecretion of the glucocorticoid hormone cortisol leads to a disorder called Cushing’s syndrome. The most common cause of Cushing’s syndrome is a pituitary tumor, which causes excessive production of ACTH. The disease produces a wide variety of signs and symptoms, which may include obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure (hypertension), excessive body hair, osteoporosis, and depression. A distinctive sign of Cushing’s syndrome is the appearance of stretch marks in the skin, as the skin becomes progressively thinner. Another distinctive sign is a moon face, in which fat deposits give the face a rounded appearance. Treatment of Cushing’s syndrome depends on its cause and may include surgery to remove a tumor or medications to suppress activity of the adrenal glands.
Adrenal Hyposecretion: Addison’s Disease

Hyposecretion of the glucocorticoid hormone cortisol leads to a disorder called Addison’s disease. There may also be hyposecretion of mineralocorticoids with this disorder. Addison’s disease is generally an autoimmune disorder, in which the immune system produces abnormal antibodies that attack cells of the adrenal cortex. Untreated infections, especially of tuberculosis, may also damage the adrenal cortex and cause Addison’s disease. A third possible cause is decreased output of ACTH by the pituitary gland, generally due to a pituitary tumor. A distinctive sign of Addison’s disease is hyperpigmentation of the skin (see the photos in Figure 9.6.6). Other symptoms tend to be nonspecific and include excessive fatigue. Addison’s disease is generally treated with replacement hormones in pill form.
Feature: My Human Body

Does just looking at this photo (Figure 9.6.7) cause you to break out in a cold sweat and experience heart palpitations? Imagine how scary it would be to actually fling yourself backward off a tall building like the BASE jumper in the photo! There would be very little time to use a parachute to slow your fall before you hit the ground. BASE jumping is called the most dangerous sport on Earth. In fact, it is so dangerous that it is outlawed in some places.
People who participate in such dangerous activities as BASE jumping are likely to be adrenaline “junkies.” They are addicted to the adrenaline rush and euphoria — or “high” — it causes when their fight-or-flight response is triggered by danger. Why does adrenaline have this effect? Adrenaline is closely related to dopamine, a chemical messenger in the brain that plays a major role in pleasure and addiction.
Adrenaline addicts don’t have to participate in BASE jumping or other dangerous sports to get an adrenaline rush. They might choose a dangerous occupation like firefighting, participate in risky behaviors like reckless driving or bank robbing, or just pick fights with other people. They might even create their own stress by always taking on too much work or delaying projects until close to their deadline.
While some excitement in one’s life is generally a good thing, always putting oneself in danger or constantly being under stress are obviously not good things. If you think you might be an adrenaline addict, note that there are healthier ways to experience a hormonal “high.” Running, biking, or participating in some other form of vigorous aerobic exercise causes the pituitary gland and hypothalamus to produce opiate-like endorphins, leading to a so-called “runner’s high.” Like the euphoric feeling adrenaline causes, a runner’s high may last for hours.
9.6 Summary
- The adrenal glands are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones. The two adrenal glands are located on both sides of the body, just above the kidneys. Each gland has two layers: an outer layer called the adrenal cortex and an inner layer called the adrenal medulla.
- The adrenal cortex produces steroid hormones called by the general term corticosteroids, of which there are three types: mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone), which helps control electrolyte balance; glucocorticoids (such as cortisol), which helps control the rate of metabolism, suppresses the immune system, and is the major stress hormone; and androgens (such as DHEA), which is converted to sex hormones in the gonads.
- The adrenal medulla produces non-steroid catecholamine hormones, including adrenaline and noradrenaline. These hormones stimulate the fight-or-flight response.
- Disorders of the adrenal glands generally include either hypersecretion or hyposecretion of adrenal hormones. The cause may be a problem with the adrenal glands or with the pituitary gland, which controls adrenal cortex hormone production. Examples include Cushing’s syndrome, in which there is hypersecretion of cortisol, and Addison’s disease, in which there is hyposecretion of cortisol and mineralocorticoids.
9.6 Review Questions
- Describe the structure and location of the adrenal glands.
-
- Compare and contrast the adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla.
- Identify the three layers of the adrenal cortex and the type of hormones each layer produces.
- Give an example of each type of corticosteroid and state its function.
- Explain how the production of glucocorticoids is regulated.
- What is a catecholamine? Give an example of a catecholamine and state its function.
- Compare and contrast Cushing’s syndrome and Addison’s disease.
- What are two ways in which the nervous system (which includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves) controls the adrenal gland?
- Explain why a pituitary tumor can cause either hypersecretion or hyposecretion of cortisol.
9.6 Explore More
How stress affects your body – Sharon Horesh Bergquist, TED-Ed, 2015.
How stress affects your brain – Madhumita Murgia, TED-Ed, 2015.
Adrenaline: Fight or Flight Response, Henk van ‘t Klooster, 2013.
Attributions
Figure 9.6.1
Attack from wikimedia commons by Jerry Kirkhart from Los Osos, Calif. on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0) license.
Figure 9.6.2
Diagram_showing_where_the_adrenal_glands_are_in_the_body_CRUK_415.svg by Cancer Research UK uploader on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 9.6.3
Adrenal_cortex_labelled by Jpogi at English Wikipedia on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication (https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en) license.
Figure 9.6.4
The_Adrenal_Glands by OpenStax College is used under a CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) license.
Figure 9.6.5
ACTH negative feedback loop by Christinelmiller is used under a CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) license.
Figure 9.6.6
A_69-Year-Old_Female_with_Tiredness_and_a_Persistent_Tan_01 by Petros Perros on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 2.5 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5/deed.en) license.
Figure 9.6.7
BASE_Jumping_from_Sapphire_Tower_in_Istanbul by Kontizas Dimitrios on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0) license.
References
Betts, J. G., Young, K.A., Wise, J.A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Kruse, D.H., Korol, O., Johnson, J.E., Womble, M., DeSaix, P. (2013, June 19). Figure 17.17 Adrenal glands [digital image]. In Anatomy and Physiology (Section 17.6). OpenStax College. https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/17-6-the-adrenal-glands
Henk van ‘t Klooster. (2013). Adrenaline: Fight or flight response. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FBnBTkcr6No&feature=youtu.be
Perros, P. (2005). A 69-year-old female with tiredness and a persistent tan. PLoS Medicine, 2(8): e229. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0020229
TED-Ed. (2015, October 22). How stress affects your body – Sharon Horesh Bergquist. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v-t1Z5-oPtU&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2015, November 6). How stress affects your brain – Madhumita Murgia. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WuyPuH9ojCE&feature=youtu.be
An involuntary human body response mediated by the nervous and endocrine systems that prepares the body to fight or flee from perceived danger.
one of a pair of glands located on top of the kidneys that secretes hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline
The outer layer of the adrenal gland that produces steroid hormones such as cortisol and aldosterone.
The outermost layer of the adrenal cortex. It lies immediately under the outer fibrous capsule that encloses the adrenal gland.
The middle layer of the adrenal cortex. It is the largest of the three zones, accounting for nearly 80% of the adrenal cortex.
The innermost layer of the adrenal cortex. It is directly adjacent to the medulla of the adrenal gland.
Any steroid hormone produced by the cortex of the adrenal gland; includes mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens.
A type of endocrine hormone that is made of lipids and crosses the plasma membrane to bind with a receptor inside a target cell.
A substance that is insoluble in water. Examples include fats, oils and cholesterol. Lipids are made from monomers such as glycerol and fatty acids.
A type of cell on which a particular hormone has an effect because it has receptor molecules for the hormone.
A semi-permeable lipid bilayer that separates the interior of all cells from their surroundings.
A central organelle containing hereditary material.
The process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional protein.
The main mineralocorticoid hormone which is responsible for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands and colon.
A glucocorticoid hormone produced by the cortex of the adrenal gland that is released in response to stress and also helps control metabolic rate, suppression of the immune system, and other functions
A class of biological molecule consisting of linked monomers of amino acids and which are the most versatile macromolecules in living systems and serve crucial functions in essentially all biological processes.
Glucose (also called dextrose) is a simple sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight.
Long chains of hydrocarbons with a carboxyl group and a methyl group at opposite ends. Can be either saturated, containing mostly single bonds between adjacent carbons, or unsaturated, containing many double bonds between adjacent carbons.
The general term for a sex hormone predominant in males, such as testosterone.
The male sex hormone secreted mainly by the testes.
Two male reproductive organs that produce sperm and secrete testosterone; male gonad.
The female sex hormone secreted mainly by the ovaries.
A pair of female reproductive organs that produces eggs and secretes estrogen.
The front lobe of the pituitary gland that synthesizes and secretes pituitary hormones.
A control mechanism that serves to reduce an excessive response and keep a variable within its normal range.
A part of the brain that secretes hormones and connects the brain with the endocrine system.
The central part of an adrenal gland that is surrounded by the adrenal cortex and that produces catecholamine hormones including adrenaline.
A class of molecules that includes the non-steroid hormones produced by the medulla of the adrenal gland, such as adrenaline, that stimulate the fight-or-flight response.
A non-steroid catecholamine hormone produced by the medulla of the adrenal glands that stimulates the fight-or-flight response.
A substance that is released predominantly from the ends of sympathetic nerve fibres and that acts to increase the force of skeletal muscle contraction and the rate and force of contraction of the heart.
Any type of endocrine hormone that is made of amino acids and binds with a receptor on the plasma membrane of a target cell.
Amino acids are organic compounds that combine to form proteins.
The division of the autonomic nervous system that controls the fight-or-flight response.
division of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary activities
A secretion of more than the normal amount of a substance, such as secretion of too much hormone by an endocrine gland.
The secretion of less than the normal amount of a substance, such as secretion of too much hormone by an endocrine gland.
A disorder in which there is hypersecretion of the adrenal cortex hormone cortisol, most commonly due to a tumor of the pituitary gland.
A disorder characterized by hyposecretion of the adrenal cortex hormone cortisol, generally because the immune system attacks and destroys the adrenal gland.

