126 16.11 Energy in Waves: Intensity
Summary
- Calculate the intensity and the power of rays and waves.

All waves carry energy. The energy of some waves can be directly observed. Earthquakes can shake whole cities to the ground, performing the work of thousands of wrecking balls.
Loud sounds pulverize nerve cells in the inner ear, causing permanent hearing loss. Ultrasound is used for deep-heat treatment of muscle strains. A laser beam can burn away a malignancy. Water waves chew up beaches.
The amount of energy in a wave is related to its amplitude. Large-amplitude earthquakes produce large ground displacements. Loud sounds have higher pressure amplitudes and come from larger-amplitude source vibrations than soft sounds. Large ocean breakers churn up the shore more than small ones. More quantitatively, a wave is a displacement that is resisted by a restoring force. The larger the displacement [latex]{x},[/latex] the larger the force [latex]{F=kx}[/latex] needed to create it. Because work [latex]{W}[/latex] is related to force multiplied by distance [latex]({Fx})[/latex] and energy is put into the wave by the work done to create it, the energy in a wave is related to amplitude. In fact, a wave’s energy is directly proportional to its amplitude squared because
The energy effects of a wave depend on time as well as amplitude. For example, the longer deep-heat ultrasound is applied, the more energy it transfers. Waves can also be concentrated or spread out. Sunlight, for example, can be focused to burn wood. Earthquakes spread out, so they do less damage the farther they get from the source. In both cases, changing the area the waves cover has important effects. All these pertinent factors are included in the definition of intensity [latex]{I}[/latex] as power per unit area:
where [latex]{P}[/latex] is the power carried by the wave through area [latex]{A}.[/latex] The definition of intensity is valid for any energy in transit, including that carried by waves. The SI unit for intensity is watts per square meter ( [latex]{\text{W/m}^2}[/latex] ). For example, infrared and visible energy from the Sun impinge on Earth at an intensity of [latex]{1300\text{ W/m}^2}[/latex] just above the atmosphere. There are other intensity-related units in use, too. The most common is the decibel. For example, a 90 decibel sound level corresponds to an intensity of [latex]{10^{-3}\text{ W/m}^2}.[/latex] (This quantity is not much power per unit area considering that 90 decibels is a relatively high sound level. Decibels will be discussed in some detail in a later chapter.
Example 1: Calculating intensity and power: How much energy is in a ray of Sunlight?
The average intensity of sunlight on Earth’s surface is about [latex]{700\text{ W/m}^2}.[/latex]
(a) Calculate the amount of energy that falls on a solar collector having an area of [latex]{0.500\text{ m}^2}[/latex] in [latex]{4.00\text{ h}}.[/latex]
(b) What intensity would such sunlight have if concentrated by a magnifying glass onto an area 200 times smaller than its own?
Strategy a
Because power is energy per unit time or [latex]{P=\frac{E}{t}},[/latex] the definition of intensity can be written as [latex]{I=\frac{P}{A}=\frac{E/t}{A}},[/latex] and this equation can be solved for E with the given information.
Solution a
- Begin with the equation that states the definition of intensity:
[latex]{I\:=}[/latex] [latex]{\frac{P}{A}}.[/latex]
- Replace [latex]{P}[/latex] with its equivalent [latex]{E/t}:[/latex]
[latex]{I\:=}[/latex] [latex]{\frac{E/t}{A}}.[/latex]
- Solve for [latex]{E}:[/latex]
[latex]{E=IAt}.[/latex]
- Substitute known values into the equation:
[latex]{E=(700\text{ W/m}^2)(0.500\text{ m}^2)[(4.00\text{ h})(3600\text{ s/h})]}.[/latex]
- Calculate to find [latex]{E}[/latex] and convert units:
[latex]{5.04\times10^6\text{ J}},[/latex]
Discussion a
The energy falling on the solar collector in 4 h in part is enough to be useful—for example, for heating a significant amount of water.
Strategy b
Taking a ratio of new intensity to old intensity and using primes for the new quantities, we will find that it depends on the ratio of the areas. All other quantities will cancel.
Solution b
- Take the ratio of intensities, which yields:
[latex]{\frac{I^{\prime}}{I}}[/latex] [latex]{=}[/latex] [latex]{\frac{P^{\prime}/A^{\prime}}{P/A}}[/latex] [latex]{=}[/latex] [latex]{\frac{A}{A^{\prime}}}([/latex] [latex]{\text{The powers cancel because }P^{\prime}=P}[/latex] [latex]).[/latex]
- Identify the knowns:
[latex]{A=200A^{\prime}},[/latex][latex]{\frac{I^{\prime}}{I}}[/latex] [latex]{=200}.[/latex]
- Substitute known quantities:
[latex]{I^{\prime}=200I=200(700\text{ W/m}^2)}.[/latex]
- Calculate to find [latex]{I^{\prime}}:[/latex]
[latex]{I^{\prime}=1.40\times10^5\text{ W/m}^2}.[/latex]
Discussion b
Decreasing the area increases the intensity considerably. The intensity of the concentrated sunlight could even start a fire.
Example 2: Determine the combined intensity of two waves: Perfect constructive interference
If two identical waves, each having an intensity of [latex]{1.00\text{ W/m}^2},[/latex] interfere perfectly constructively, what is the intensity of the resulting wave?
Strategy
We know from Chapter 16.10 Superposition and Interference that when two identical waves, which have equal amplitudes [latex]{X},[/latex] interfere perfectly constructively, the resulting wave has an amplitude of [latex]{2X}.[/latex] Because a wave’s intensity is proportional to amplitude squared, the intensity of the resulting wave is four times as great as in the individual waves.
Solution
- Recall that intensity is proportional to amplitude squared.
- Calculate the new amplitude:
[latex]{I^{\prime}\propto(X^{\prime})^2=(2X)^2=4X^2}.[/latex]
- Recall that the intensity of the old amplitude was:
[latex]{I\propto{X}^2}.[/latex]
- Take the ratio of new intensity to the old intensity. This gives:
[latex]{\frac{I^{\prime}}{I}}[/latex] [latex]{=4}.[/latex]
- Calculate to find [latex]{I^{\prime}}:[/latex]
[latex]{I^{\prime}=4I=4.00\text{ W/m}^2}.[/latex]
Discussion
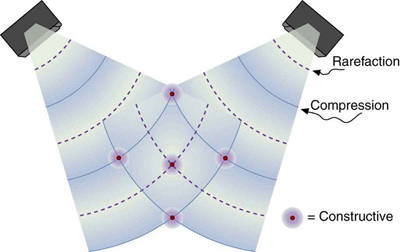
The intensity goes up by a factor of 4 when the amplitude doubles. This answer is a little disquieting. The two individual waves each have intensities of [latex]{1.00\text{ W/m}^2},[/latex] yet their sum has an intensity of [latex]{4.00\text{ W/m}^2},[/latex] which may appear to violate conservation of energy. This violation, of course, cannot happen. What does happen is intriguing. The area over which the intensity is [latex]{4.00\text{ W/m}^2}[/latex] is much less than the area covered by the two waves before they interfered. There are other areas where the intensity is zero. The addition of waves is not as simple as our first look in Chapter 16.10 Superposition and Interference suggested. We actually get a pattern of both constructive interference and destructive interference whenever two waves are added. For example, if we have two stereo speakers putting out [latex]{1.00\text{ W/m}^2}[/latex] each, there will be places in the room where the intensity is [latex]{4.00\text{ W/m}^2},[/latex] other places where the intensity is zero, and others in between. Figure 2 shows what this interference might look like. We will pursue interference patterns elsewhere in this text.
Check Your Understanding
1: Which measurement of a wave is most important when determining the wave's intensity?
Section Summary
Intensity is defined to be the power per unit area:
[latex]{I=\frac{P}{A}}[/latex] and has units of [latex]{\text{W/m}^2}.[/latex]
Conceptual Questions
1: Two identical waves undergo pure constructive interference. Is the resultant intensity twice that of the individual waves? Explain your answer.
2: Circular water waves decrease in amplitude as they move away from where a rock is dropped. Explain why.
Exercises
1: Medical Application
Ultrasound of intensity [latex]{1.50\times10^2\text{ W/m}^2}[/latex] is produced by the rectangular head of a medical imaging device measuring 3.00 by 5.00 cm. What is its power output?
2: The low-frequency speaker of a stereo set has a surface area of [latex]{0.05\text{ m}^2}[/latex] and produces 1W of acoustical power. What is the intensity at the speaker? If the speaker projects sound uniformly in all directions, at what distance from the speaker is the intensity [latex]{0.1\text{ W/m}^2}?[/latex]
3: To increase intensity of a wave by a factor of 50, by what factor should the amplitude be increased?
4: Engineering Application
A device called an insolation meter is used to measure the intensity of sunlight has an area of 100 cm2 and registers 6.50 W. What is the intensity in [latex]{\text{W/m}^2}?[/latex]
5: Astronomy Application
Energy from the Sun arrives at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere with an intensity of [latex]{1.30\text{ kW/m}^2}.[/latex] How long does it take for [latex]{1.8\times10^9\text{ J}}[/latex] to arrive on an area of [latex]{1.00\text{ m}^2}?[/latex]
6: Suppose you have a device that extracts energy from ocean breakers in direct proportion to their intensity. If the device produces 10.0 kW of power on a day when the breakers are 1.20 m high, how much will it produce when they are 0.600 m high?
7: Engineering Application
(a) A photovoltaic array of (solar cells) is 10.0% efficient in gathering solar energy and converting it to electricity. If the average intensity of sunlight on one day is [latex]{700\text{ W/m}^2},[/latex] what area should your array have to gather energy at the rate of 100 W? (b) What is the maximum cost of the array if it must pay for itself in two years of operation averaging 10.0 hours per day? Assume that it earns money at the rate of 9.00 ¢ per kilowatt-hour.
8: A microphone receiving a pure sound tone feeds an oscilloscope, producing a wave on its screen. If the sound intensity is originally [latex]{2.00\times10^{-5}\text{ W/m}^2},[/latex] but is turned up until the amplitude increases by 30.0%, what is the new intensity?
9: Medical Application
(a) What is the intensity in [latex]{\text{W/m}^2}[/latex] of a laser beam used to burn away cancerous tissue that, when 90.0% absorbed, puts 500 J of energy into a circular spot 2.00 mm in diameter in 4.00 s? (b) Discuss how this intensity compares to the average intensity of sunlight (about [latex]{700\text{ W/m}^2}[/latex] ) and the implications that would have if the laser beam entered your eye. Note how your answer depends on the time duration of the exposure.
Glossary
- intensity
- power per unit area
Solutions
Check Your Understanding
1: Amplitude, because a wave’s energy is directly proportional to its amplitude squared.
Problems & Exercises
1:
0.225 W
3:
7.07
5:
16.0 d
6:
2.50 kW
8:
[latex]{3.38\times10^{-5}\text{ W/m}^2}[/latex]

